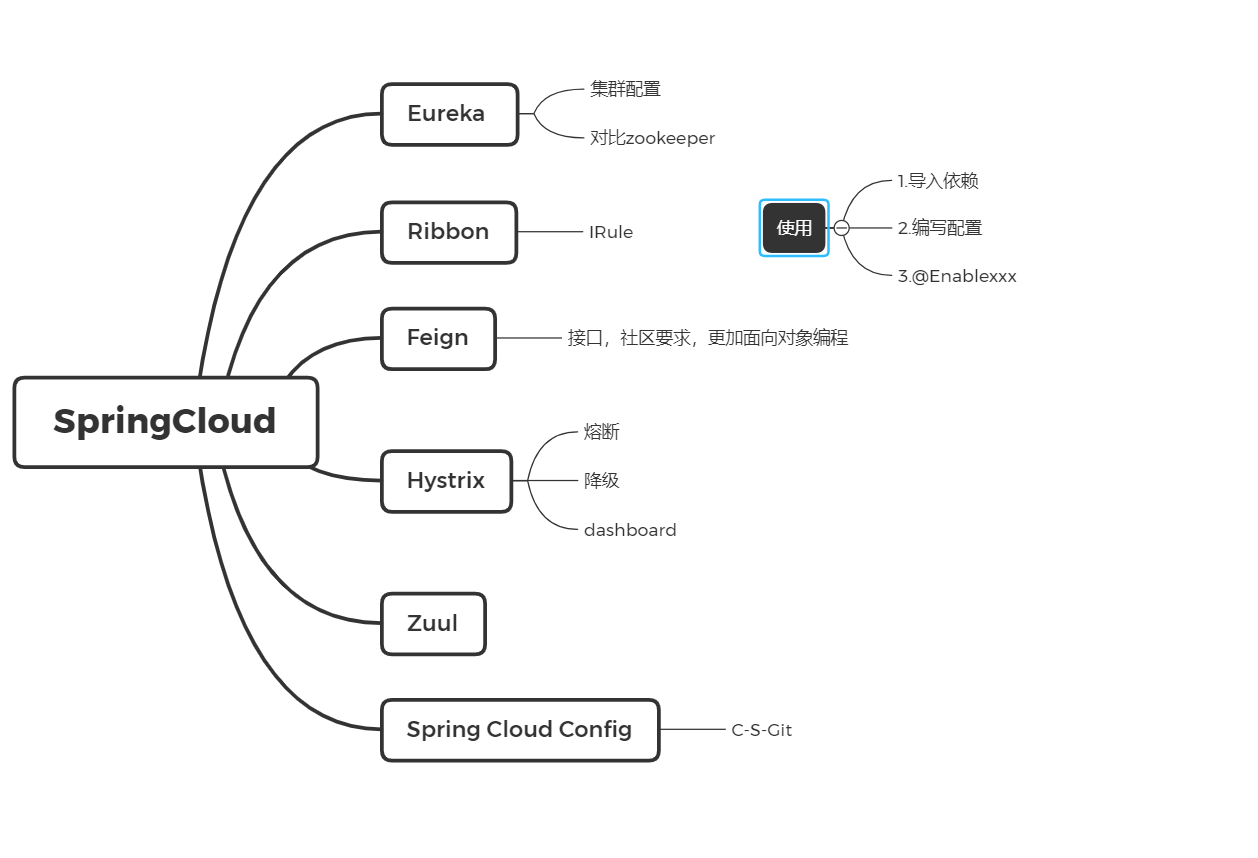
SpringCloud
微服务架构4个核心问题?
- 服务很多,客户端该怎么访问?
- 这么多服务?服务之间如何通信?
- 这么多服务? 如何治理?
- 服务挂了怎么办?
解决方案:Spring Cloud生态!
Spring Cloud NetFlix一站式解决方案!
api网关,zuu1组件
Feign —Httpclinet —- Http通信方式,同步,阻塞
服务注册发现: Eureka
熔断机制: Hystrix
Apache Dubbo Zookeeper半自动,需要整个别人的
API:没有,找第三方组件,或者自己实现
Dubbo
Zookeeper
没有:借助Hystrix
Dubbo这个方案并不完善~
spring Cloud Alibaba一站式解决方案
新概念:服务网格~Server Mesh
istio
万变不离其宗 1. API 2. HTTP,RPC 3. 注册和发现 4. 熔断机制
归根结底的原因是:网络不可靠!
微服务概述
什么是微服务
什么是微服务?微服务(Microservice Architecture)是近几年流行的一种架构思想,关于它的概念很难一言以蔽 之。
究竟什么是微服务呢?我们在此引用ThoughtWorks公司的首席科学家Martin Fowler于2014年提出的- -段话:
- 就目前而言,对于微服务,业界并没有一个统- -的, 标准的定义
- 但通常而言,微服务架构是一 种架构模式,或者说是一-种架构风格, 它提倡将单- -的应用程序划分成- -组小 的服务,每个服务运行在其独立的自己的进程内,服务之间互相协调,互相配置,为用户提供最终价值。服务 之间采用轻量级的通信机制互相沟通,每个服务都围绕着具体的业务进行构建,并且能够被独立的部署到生产 环境中,另外,应尽量避免统- -的,集中式的服务管理机制,对具体的一个服务而言,应根据业务上下文,选 择合适的语言,工具对其进行构建,可以有一个非常轻 量级的集中式管理来协调这些服务,可以使用不同的语 言来编写服务,也可以使用不同的数据存储;
可能有的人觉得官方的话太过生涩,我们从技术维度来理解下:
微服务化的核心就是将传统的一站式应用,根据业务拆分成: 个一 的服务,彻底地去耦合,每一个微服务提 供单个业务功能的服务,-个服务做-件事情,无识别结果种小而独立的处理过程,类似进程的概念,能够自行单独启动或销毁,拥有自己独立的数据库。
微服务与微服务架构
微服务
强调的是服务的大小,他关注的是某-个点, 是具体解决某-个问题/提供落地对应服务的- 一个服务应用,狭义的 看,可以看做是IDEA中的-一个个微服务工程,或者Moudel
IDEA工具里面使用Maven开发的一个个独立的小Moudle, 它具体是使用springboot开发的一个小模块,专业的事 情交给专业的模块来做,- 一个模块就做着一 -件事情
强调的是-一个个的个体,每个个体完成-一个具体的任务或者功能!
微服务架构
一种新的架构形式,Martin Fowler, 2014提出
微服务优缺点
优点
- 每个服务足够内聚,足够小,代码容易理解,这样能聚焦-个指定的业务功能或业务需求;
- 开发简单,开发效率提高,-个服务可能就是专- -的只干一 -件事;
- 微服务能够被小团队单独开发,这个小团队是2~5人的开发人员组成;
- 微服务是松耦合的,是有功能意义的服务,无论是在开发阶段或部署阶段都是独立的。
- 微服务能使用不同的语言开发。
- 易于和第三方集成,微服务允许容易且灵活的方式集成自动部署,通过持续集成工具,如jenkins, Hudson, bamboo
- 微服务易于被一个开发人员理解,修改和维护,这样小团队能够更关注自己的工作成果。无需通过合作才能体 现价值。
- 微服务允许你利用融合最新技术。
- 微服务只是业务逻辑的代码,不会和HTML,CSsS 或其他界面混合
- 每个微服务都有自己的存储能力,可以有自己的数据库,也可以有统- -数据库
缺点:
- 开发人员要处理分布式系统的复杂性
- 多服务运维难度,随着服务的增加,运维的压力也在增大
- 系统部署依赖
- 服务间通信成本
- 数据一致性
- 系统集成测试
- 性能监控.
微服务技术
| 微服务条目 | 落地技术 |
|---|---|
| 微服务开发 | springBoot、Spring、SpringMVC |
| 服务配置与管理 | Netflix公司的Archaius、阿里的Diamond等 |
| 服务注册与发现 | Eureka、Consul、Zookeeper等 |
| 服务调用 | Rest、RPC、gGPC |
| 服务熔断器 | Hystrix、Envoy等 |
| 负载均衡 | Ribbon、Nginx等 |
| 服务接口调用(客户端调用服务的简化工具) | Feign等 |
| 消息队列 | kafka、rabbitMQ、Chef等 |
| 服务配置中心管理 | Zuul等 |
| 服务路由(API网关) | Zabbix、Nagios、Metrics、Specatator等 |
| 服务监控 | Ziokin、Brave、Dapper |
| 全链路追踪 | Docker、OpenStack、Kubernets等 |
| 服务部署 | SpringCloud Stream(封装Redis、Rabbit、Kafka等发送接收消息) |
| 数据流操作开发包 | SpringCloud Bus |
| 时间消息总线 |
为什么选择SpringCloud作为微服务架构
选型依据
整体解决方案和框架成熟度
社区热度
可维护性
学习曲线 当前各大IT公司用的微服务架构有哪些?
- 阿里: dubbo+HFS
- 京东: JSF
- 新浪: Motan
- 当当网DubboX
各微服务框架对比
| 功能点/服务框架 | Netfix/SpringCloud | Motan | gRPC | Thrift | Dubbo/DubboX |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 功能定位 | 完整的微服务架构 | RPC框架,但整合了ZK或Consul,实现集群环境的基本服务注册/发现 | RPC框架 | RPC框架 | 服务框架 |
| 支持Rest | 是,Ribbon支持多种可拔插的序列化选择 | 否 | 否 | 否 | 否 |
| 支持RPC | 否 | 是(Hession2)是 | 是 | 是 | 是 |
| 支持多语言 | 是(Rest形式) | 否 | 是 | 是 | 否 |
| 负载均衡 | 是(服务端zuul+客户端Ribbon),zuul-服务,动态路由,云端负载均衡Eureka(针对中间层服务器) | 是(客户端) | 否 | 否 | 是(客户端) |
| 配置服务 | NEtfix Archaius,Spring Cloud Config Server集中配置 | 是(Zookeeper提供) | 否 | 否 | 否 |
| 服务调用链监控 | 是(zuul),zuul提供边缘服务,API网关 | 否 | 否 | 否 | 否 |
| 高可用/容错 | 是(服务端Hystrlx+服务端Ribbon) | 是(客户端) | 否 | 否 | 是(客户端) |
| 典型应用案例 | Netflix | Sina | |||
| 社区活跃程度 | 高 | 一般 | 高 | 一般 | 2017年后重启开始维护,之前终段了五年 |
| 学习难度 | 中等 | 低 | 高 | 高 | 低 |
| 文档丰富程度 | 高 | 一般 | 一般 | 一般 | 高 |
| 其他 | Spring Cloud Bus为我们的应用程序带来了更多管理端点 | 支持降级 | Netflix内部再开发继承gRPC | IDL定义 | 时间的公司比较多 |
SpringCloud入门概述
SpringCloud是什么
SpringCloiud,基于SpringBoot提供了-套微服务解决方案,包括服务注册与发现,配置中心,全链路监控,服务 网关,负载均衡,熔断器等组件,除了基于NetFlix的开源组件做高度抽象封装之外,还有一些选型中立的开源组 件。
SpringCloud利用SpringBoot的开发便利性,巧妙地简化了分布式系统基础设施的开发, SpringCloud为开发人员 提供了快速构建分布式系统的-些工具,包括配置管理,服务发现,断路器,路由,微代理,事件总线,全局锁, 决策竞选,分布式会话等等,他们都可以用SpringBoot的开发风格做到一-键启动和部署。
SpringBoot并没有重复造轮子,它只是将目前各家公司开发的比较成熟,经得起实际考研的服务框架组合起来, 通过SpringBoot风格进行再封装,屏蔽掉了复杂的配置和实现原理,最终给开发者留出了一套简单易懂,易部署 和易维护的分布式系统开发工具包
SpringCloud是分布式微服务架构下的一-站式解决方案,是各个微服务架构落地技术的集合体,俗称微服务全家 桶。
SpringCloud和SpringBoot关系
- SpringBoot专注于 快速方便的开发单个个体微服务。
- SpringCloud是关注全 局的微服务协调整理治理框架,它将SpringBoot开发的一 个个单体微服务整合并管理起 来,为各个微服务之间提供:配置管理,服务发现,断路器,路由,微代理,事件总线,全局锁,决策竞选, 分布式会话等等集成服务。
SpringBoot可以离开SpringClooud独立使用,开发项目,但是SpringCloud离不开SpringBoot, 属于依赖关 系
SpringBoot专注于快速、 方便的开发单个个体微服务, SpringCloud关注全 局的服务治理框架
Dubbo 和SpringCloud技术选型
分布式+服务治理Dubbo
目前成熟的互联网架构:应用服务化拆分+消息中间件
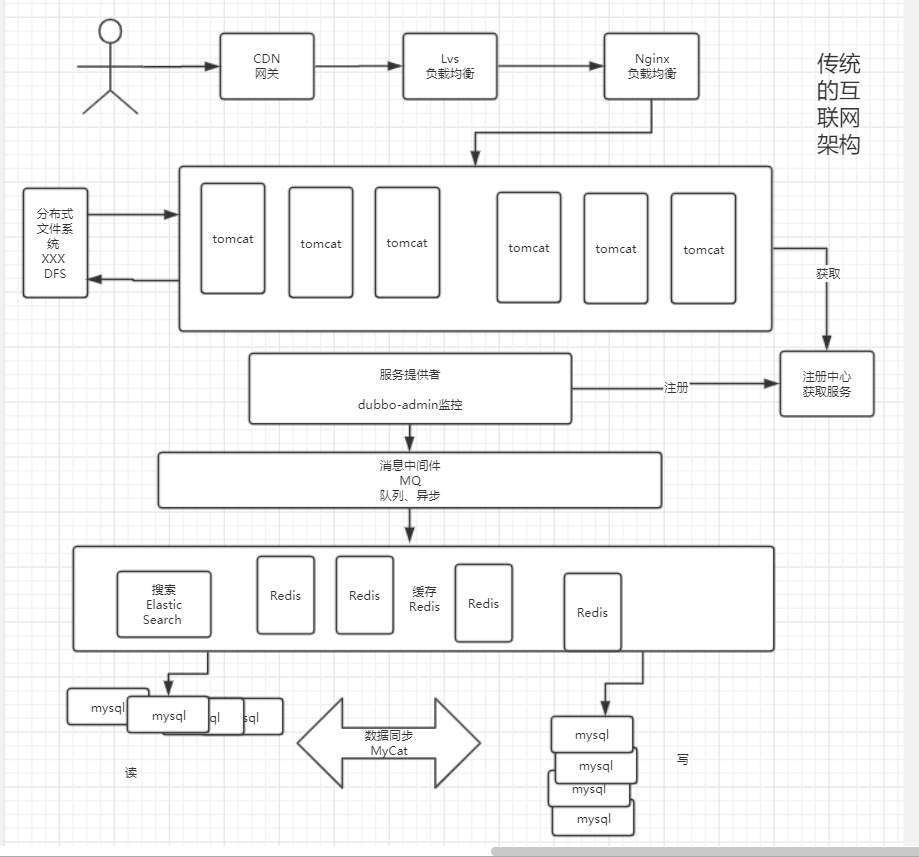
Dubbo和SpringCloud对比
可以看一- 下社区活跃度
https://github.com/spring-cloud
结果:
| Dubbo | Spring | |
|---|---|---|
| 服务注册中心 | Zookeeper | Spring Cloud Netflix Eureka |
| 服务调用方式 | RPC | REST API |
| 服务监控 | Dubbo-monitor | Spring Boot Admin |
| 短路器 | 不完善 | Spring Cloud Netflix Hystrix |
| 服务网关 | 无 | Spring Cloud Netflix Zuul |
| 分布式配置 | 无 | Spring Cloud Config |
| 服务追踪 | 无 | Spring Cloud Sleuth |
| 消息总线 | 无 | Spring Cloud Bus |
| 数据流 | 无 | Spring Cloud Stream |
| 批量任务 | 无 | Spring Cloud Task |
最大区别: SpringCloud抛弃 了Dubbo的RPC通信,采用的是基于HTTP的REST方式。
严格来说,这两种方式各有优劣。虽然从一定程度上来说,后者牺牲了服务调用的性能,但也避免了上面提到的原 生RPC带来的问题。而且REST相比RPC更为灵活,服务提供方和调用方的依赖只依靠一纸契约,不存在代码级别的 强依赖,这在强调快速演化的微服务环境下,显得更加合适。
品牌机与组装机的区别
很明显,Spring Cloud的功能比DUBBO更加强大,涵盖面更广,而且作为Spring的拳头项目,它也能够与Spring Framework. Spring Boot. Spring Data. Spring Batch等其他Spring项目完美融合,这些对于微服务而言是至 关重要的。使用Dubbo构建的微服务架构就像组装电脑,各环节我们的选择自由度很高,但是最终结果很有可能 因为一条内存质量不行就点不亮了,总是让人不怎么放心,但是如果你是一名高手, 那这些都不是问题;而Spring Cloud就像品牌机,在Spring Source的整合下,做了大量的兼容性测试,保证了机器拥有更高的稳定性,但是如 果要在使用非原装组件外的东西,就需要对其基础有足够的了解。
社区支持与更新力度
最为重要的是,DUBBO停止了5年左右的更新,虽然2017.7重启了。对于技术发展的新需求,需要由开发者自行 拓展升级(比如当当网弄出了DubboX),这对于很多想要采用微服务架构的中小软件组织,显然是不太合适的, 中小公司没有这么强大的技术能力去修改Dubbo源码+周边的一整套解决方案,并不是每一个公司都有阿里的大牛 +真实的线上生产环境测试过。
总结:
曾风靡国内的开源RPC服务框架Dubbo在重启维护后,令许多用户为之雀跃,但同时,也迎来了一一些质疑的声 音。互联网技术发展迅速,Dubbo 是否还能跟上时代? Dubbo与Spring Cloud相比又有何优势和差异?是否会 有相关举措保证Dubbo的后续更新频率?
人物: Dubbo重启维护开发的刘军,主要负责人之一
刘军,阿里巴巴中间件高级研发工程师,主导了Dubbo重启维护以后的几个发版计划,专注于高性能RPC框架 和微服务相关领域。曾负责网易考拉RPC框架的研发及指导在内部使用,参与了服务治理平台、分布式跟踪系 统、分布式一致性框架等从无到有的设计与开发过程。
解决的问题域不-样: Dubbo的定位是一 -款RPC框架, Spring Cloud的目标是微服务架构下的一站式解决方案
设计模式+微服务拆分思想
SpringCloud能干嘛
- Distributed/versioned configuration (分布式/版本控制配置)
- Service registration and discovery (服务注册与发现)
- Routing (路由)
- Service-to-service calls (服务到服务的调用)
- Load balancing (负载均衡配置)
- Circuit Breakers (断路器)
- Distributed messaging (分布式消息管理)
SpringCloud在哪下
官网: http://projects.spring.io/spring-cloud/
这玩意的版本号有点特别
Spring Cloud是一个由众多独立了项目组成的大型综合项目,每个了项目有不同的发行节奏,都维护着自己的发布版 本号。spring Cloud通过一个资源清单BOM (Bi11 of Materials) 来管理每个版本的子项目清单。为避免与子项 目的发布号混淆,所以没有采用版本号的方式,而是通过命名的方式。
这些版本名称的俞名方式采用了伦敦地铁站的名称,同时根据字母表的顺序来对应版本时间顺序,比如:最早的 Release版本: Ange1, 第二个Release版本: Brixton, 然后是Camden、Dalston、Edgware, 日前最新的是 Finch7ey版本。
参考书:
- https://springcloud.cc/spring-cloud-netflix.html
- 中文API文档: https://springcloud.cc/spring-cloud-dalston.html
- SpringCloud中国社区 http://springcloud.cn/
- SpringCloud中文网 https://springcloud.cc
SpringCloud版本选择
大版本说明
| Spring Boot | Spring Cloud | 关系 |
|---|---|---|
| 1.2.x | Angel版本(天使) | 兼容Spring Boot 1.2.x |
| 1.3.x | Brixton版本(布里克斯顿) | 兼容Spring Boot 1.3.x,也兼容Spring Boot 1.4.x |
| 1.4.x | Camden版本(卡姆登) | 兼容Spring Boot 1.4.x,也兼容Spring Boot 1.5.x |
| 1.5.x | Dalstion版本(多尔斯顿) | 兼容Spring Boot 1.5.x,不兼容Spring Boot 2.0.x |
| 1.5.x | Edware版本(埃奇韦尔) | 兼容Spring Boot 1.5.x,不兼容Spring Boot 2.0.x |
| 2.0.x | Funchley版本(芬奇利) | 兼容Spring Boot 2.0.x,不兼容Spring Boot 1.5.x |
| 2.1.x | GreenWich版本(格林威治) |
实际开发版本关系
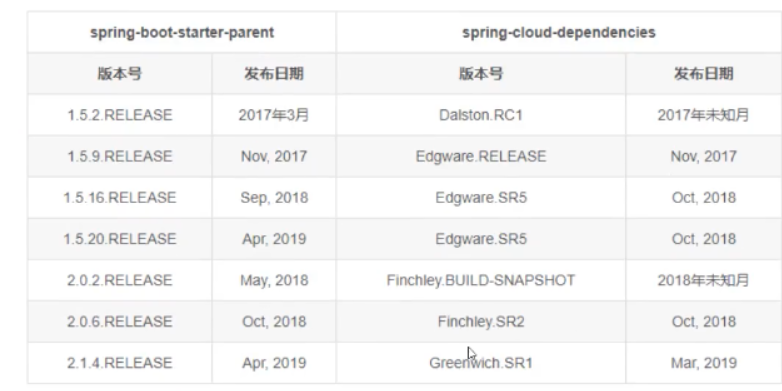
实践
第一个springCloud项目
新建一个maven的父工程
使用springcloud的版本为Greenwich.SR1
添加依赖
<!-- 打包方式-->
<packaging>pom</packaging>
<!-- 依赖版本控制-->
<properties>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
<maven.compiler.source>1.8</maven.compiler.source>
<maven.compiler.target>1.8</maven.compiler.target>
<junit.version>4.12</junit.version>
<log4j.version>1.2.17</log4j.version>
<lombok.version>1.16.20</lombok.version>
</properties>
<!-- 依赖管理-->
<dependencyManagement>
<dependencies>
<!-- springcloud的依赖-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-dependencies</artifactId>
<version>Greenwich.SR1</version>
<type>pom</type>
<scope>import</scope>
</dependency>
<!-- springboot的依赖-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-dependencies</artifactId>
<version>2.1.4.RELEASE</version>
<type>pom</type>
<scope>import</scope>
</dependency>
<!-- 数据库依赖-->
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>5.1.46</version>
</dependency>
<!-- 数据源依赖-->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>druid</artifactId>
<version>1.1.10</version>
</dependency>
<!-- springboot启动依赖-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis.spring.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>1.3.2</version>
</dependency>
<!-- junit测试依赖-->
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>${junit.version}</version>
</dependency>
<!-- lombok插件依赖-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
<version>${lombok.version}</version>
</dependency>
<!-- 日志依赖-->
<dependency>
<groupId>ch.qos.logback</groupId>
<artifactId>logback-core</artifactId>
<version>1.2.3</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>log4j</groupId>
<artifactId>log4j</artifactId>
<version>${log4j.version}</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</dependencyManagement>
新建子模块(maven)springCloud-api
添加依赖
<dependencies>
<!-- 当前的module依赖,可以导入父工程依赖(如果父工程有此依赖)-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
数据库脚本
CREATE TABLE `dept` (
`dname` varchar(60) DEFAULT NULL,
`deptno` bigint(20) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`db_source` varchar(60) DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`deptno`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=11 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8 COMMENT='部门表';
insert into `dept`(`dname`,`deptno`,`db_source`) values ('开发部',1,'db01'),('人事部',2,'db01'),('财务部',3,'db01'),('市场部',4,'db01'),('运维部',5,'db01'),('klz',10,'db01');
实体类
@Data
@NoArgsConstructor//无参构造
@Accessors(chain = true) //链式写法
//实现序列化的目的是为了保证流传输不出问题
public class Dept implements Serializable {
/**
* 链式写法
* dept.setDeptNo(11).setDname('sss').setDb_source()
*/
private long deptno; //主键
private String dname;
//这个数据存在哪个数据库
private String db_source;
/**
* 链式写法
* dept.setDeptNo(11).setDname('sss').setDb_source()
*/
public Dept(String dname) {
this.dname = dname;
}
}
新建子模块springcloud-provider-dept-8001(可以加上端口名)
添加依赖
<dependencies>
<!-- 我们要拿到实体类,所以要配置api Module-->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.mumulx</groupId>
<artifactId>springCloud-api</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
</dependency>
<!--junit-->
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!--mysql-->
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!--数据源-->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>druid</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- 日志-->
<dependency>
<groupId>ch.qos.logback</groupId>
<artifactId>logback-core</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!--mybatis-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis.spring.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!--test-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!--web-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.shiro</groupId>
<artifactId>shiro-spring-boot-web-starter</artifactId>
<version>1.4.0</version>
</dependency>
<!--web容器jetty-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-jetty</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- 热部署-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-devtools</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
server:
port: 8001
# mybatis配置文件
mybatis:
type-aliases-package: com.mumulx.springCloud.pojo
config-location: classpath:mybatis/mybatis-config.xml
mapper-locations: classpath:mybatis/mapper/*.xml
#spring配置
spring:
application:
name: springboot-cloud-provider-dept
datasource:
type: com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource
driver-class-name: org.gjt.mm.mysql.Driver
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/db01?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf-8
username: root
password: 111111
mybatis配置
<!DOCTYPE configuration
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd">
<configuration>
<settings>
<!-- 设置二级缓存-->
<setting name="cacheEnabled" value="true"/>
</settings>
</configuration>
消费者
添加依赖
<dependencies>
<!-- 实体类依赖,从api中导-->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.mumulx</groupId>
<artifactId>springcloud-api</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
</dependency>
<!-- spirngboot的web依赖-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- 热部署依赖-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-devtools</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
配置
@Configuration
public class ConfigBean {
@Bean
public RestTemplate getRestTemplate() {
return new RestTemplate();
}
}
@RestController
public class DeptConsumerController {
//消费者 没有servicec层
//RestTemplate ...方法供我们调用就可以了! 注册sring中
//(url, 实体: Map, Class<T> ResponseType)
@Autowired
private RestTemplate restTemplate;
private static final String REST_URL_PREFIX = "http://localhost:8001";
@RequestMapping("/consumer/dept/get/{id}")
public Dept get(@PathVariable("id") Long id) {
return restTemplate.getForObject(REST_URL_PREFIX + "/dept/get/"+id, Dept.class);
}
@RequestMapping("/consumer/dept/add")
public boolean add(Dept dept) {
return restTemplate.postForObject(REST_URL_PREFIX +"/dept/add", dept, boolean.class);
}
@RequestMapping("/consumer/dept/list")
public List<Dept> list() {
return restTemplate.getForObject(REST_URL_PREFIX + "/dept/list", List.class);
}
}
消费者 没有servicec层
RestTemplate …方法供我们调用就可以了! 注册sring中
(url, 实体: Map, Class
Eureka服务注册与发现
什么是Eureka
- Eureka: 怎么读?
- Netflix 在设计Eureka时,遵循的就是AP原则
- Eureka是Netflix的一 -个子模块, I也是核心模块之-。Eureka是一 个基于REST的服务,用于定位服务,以实现 云端中间层服务发现和故障转移,服务注册与发现对于微服务来说是非常重要的,有了服务发现与注册,只需 要使用服务的标识符,就可以访问到服务,而不需要修改服务调用的配置文件了,功能类似于Dubbo的注册 中心,比如Zookeeper;
原理讲解
Eureka的基本架构
- SpringCloud 封装了NetFlix公司开发的Eureka模块来实现服务注册和发现(对比Zookeeper)
- Eureka采用了C-S的架构设计,EurekaServer 作为服务注册功能的服务器,他是服务注册中心
而系统中的其他微服务。使用Eureka的客户端连接到EurekaServer并维持心跳连接。 这样系统的维护人 员就可以通过EurekaServer来监控系统中各个微服务是否正常运行,SpringCloud的一 些其他模块(比如 Zuu)_就可以通过EurekaServer来发现系统中的其他微服务,并执行相关的逻辑:
Eureka 包含两个组件: Eureka Server和Eureka Client。
Eureka Server提供服务注册服务,各个节点启动后,会在EurekaServer中进行注册, 这样Eureka Server 中的服务注册表中将会村粗所有可用服务节点的信息,服务节点的信息可以在界面中直观的看到。
Eureka Client是-个Java客户端,用于简化EurekaServer的交互, 客户端同时也具备- -个内置的,使用轮 询负载算法的负载均衡器。在应用启动后,将会向EurekaServer发送心跳(默认周期为30秒)。如果 Eureka Server在多个心跳周期内没有接收到某个节点的心跳,EurekaServer将 会从服务注册表中把这个 服务节点移除掉(默认周期为90秒)
三大角色
- Eureka Server:提供服务的注册于发现。
- Service Provider:将自身服务注册到Eureka中,从而使消费方能够找到。
- Service Consumer:服务消费方从Eureka中获取注册服务列表,从而找到消费服务。
新建一个项目之后的步骤
- 导入依赖
- 编写配日志文件
- 开启这个功能@Enablexxx
- 配置类
依赖
<!-- 导包-->
<!-- eureka依赖-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-eureka-server</artifactId>
<version>1.4.6.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<!-- 热部署-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-devtools</artifactId>
<scope>runtime</scope>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
配置
server:
port: 7001
#eureka配置
eureka:
instance:
hostname: localhost #Eureka服务端的实例名称,localhost代表服务器的地址,最后要换的
client:
register-with-eureka: false #表示是否向eureka注册中心注册自己
fetch-registry: false #fetch-registry如果为false, 则表示自己为注册中心
service-url: # 监控页面
defaultZone: http://${eureka.instance.hostname}:${server.port}/eureka/
访问
http://localhost:7001/
注册,服务提供方添加配置
#Eureka的配置,服务注册到哪里
eureka:
client:
service-url:
defaultZone: http://localhost:7001/eureka/
添加依赖
<!-- eureka依赖-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-eureka</artifactId>
<version>1.4.6.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
开启服务
@EnableEurekaClient//开启服务
@SpringBootApplication
public class SpringCloudProvider {
启动,先启动注册中心,在启动服务提供方
完善7001的监控信息
服务提供方添加依赖
<!-- actutor完善监控信息(erekua的status指向网页的信息依赖)-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-actuator</artifactId>
</dependency>
添加配置
#info配置
info:
app.name: mumulx-springcloud
company.name: com.mumulx
自我保护机制:好死不如赖活着
一句话总结:某时刻某一个微服务不可以用了,eureka不会立刻清理,依旧会对该微服务的信息进行保存!
默认情况下,如果EurekaServer在一 定时间内没有接收到某个微服务实例的心跳,EurekaServer将会注销该实例(默认90秒)。但是当网络分区故障发生时,微服务与Eureka之间无法正常通行,以上行为可能变得非常危险了–因为微服务本身其实是健康的,此时本不应该注销这个服务。Eureka通过 自我保护机制来解决这个问题–当EurekaServer节点在短时间内丢失过多客户端时(可能发生了网络分区故障), 那么这个节点就会进入自我保护模式。- -旦进入该模式,EurekaServer就会保护服务注册表中的信息,不再删除服务注册表中的数据(也就是不会注销任何微服务)。当网络故障恢复后,EurekaServer节 点会自动退出自我保护模式。
在自我保护模式中, EurekaServer会保护服务注册表中的信息,不再注销任何服务实例。当它收到的心跳数重新恢复到阈值以上时,该EurekaServer节 点就会自动退出自我保护模式。它的设计哲学就是宁可保留错误的服务注册信息,也不盲目注销任何可能健康的服务实例。-句话:好死不如赖活着
综上,自我保护模式是一种应对网络异常的安全保护措施。它的架构哲学是宁可同时保留所有微服务(健康的微服务和不健康的微服务都会保留),也不盲目注销任何健康的微服务。使用自我保护模式,可以让Eureka集群更加的健壮和稳定
在SpringCloud中,可以使用eureka. server. enable-self-preservation = false 禁用自我保护模式[不推荐关闭自我保护机制]
获取微服务的一些信息
//获取一些配置信息,得到具体的微服务
@Autowired
private DiscoveryClient client;
@GetMapping("/dept/discovery")
//注册进来的微服务,获取一些信息
public Object discovery() {
//获得微服务列表的清单
List<String> services = client.getServices();
System.out.println("discovery=>services" + services);
//得到一个具体的微服务信息
List<ServiceInstance> instance = client.getInstances("SPRINGCLOUD-PROVIDER-DEPT");
for (ServiceInstance serviceInstance : instance) {
System.out.println(
serviceInstance.getHost()+"\t"+
serviceInstance.getPort()+"\t"+
serviceInstance.getUri()+"\t"+
serviceInstance.getServiceId()
);
}
return this.client;
}
添加注解
@EnableDiscoveryClient//服务发现
@SpringBootApplication
eureka集群
增加7002,7003.除了端口不一样其他都是相同的
增加相互间的关系()
7003
# defaultZone: http://${eureka.instance.hostname}:${server.port}/eureka/ 单个
defaultZone: http://localhost:7001/eureka/,http://127.0.0.1:7002/eureka/ # 集群
服务提供方,分别向三个注册中心进行发送
#Eureka的配置,服务注册到哪里
eureka:
client:
service-url:
defaultZone: http://localhost:7001/eureka/,http://localhost:7002/eureka/,http://localhost:7003/eureka/ # 集群
对比zookeeper
回顾CAP原则
RDBMS (Mysql. Oracle. sqlServer) ===>ACID .
NoSQL (redis. mongdb) ===> CAP
ACID是什么?
A (Atomicity) 原子性
C (Consistency)- 致性
I (Isolation) 隔离性
D (Durability) 持久性
CAP是什么?
C (Consistency) 强-致性
A(Availability) 可用性
P (Partition tolerance) 分区容错性
CAP的三进二: CA、AP、CP
CAP理论的核心
- 一个分布式系统不可能同时很好的满足一 致性,可用性和分区容错性这三个需求
- 根据CAP原理,将NoSQL数据库分成了满足CA原则,满足CP原则和满足AP原则三大类:
- CA:单点集群,满足一致性,可用性的系统,通常可扩展性较差
- CP:满足一致性,分区容错性的系统,通常性能不是特别高
- AP:满足可用性,分区容错性的系统,通常可能对一致性要求低一些
回作为服务注册中心,Eureka比Zookeeper好在哪里?
著名的CAP理论指出,-个分布式系统不可能同时满足C (- 致性)、A (可用性)、P (容错性)。 由于分区容错性P在分布式系统中是必须要保证的,因此我们只能在A和C之间进行权衡。
- Zookeeper保证的是CP;
- Eureka保证的是AP; .
Zookeeper保证的是CP
当向注册中心查询服务列表时,我们可以容忍注册中心返回的是几分钟以前的注册信息,但不能接受服务直接down掉不可用。也就是说,服务注册功能对可用性的要求要高于一致性。 但是zk会出现这样一种情况, 当master节点因为网络故障与其他节点失去联系时,剩余节点会重新进行leader选举。问题在于,选举leader的时间太长,30~120s,且选举期间整个zk集群都是不可用的,这就导致在选举期间注册服务瘫痪。在云部署的环境下,因为网络问题使得zk集群失去master节点是较大概率会发生的事件,虽然服务最终能够恢复,但是漫长的选举时间导致的注册长期不可用是不能容忍的。
Eureka保证的是AP
Eureka看明白了这一点,因此在设计时就优先保证可用性。Eureka各个节点都是平等的,几个节点挂掉不会影响正常节点的工作,剩余的节点依然可以提供注册和查询服务。而Eureka的客户端在向某个Eureka注册时,如果发现连接失败,则会自动切换至其他节点,只要有一台Eureka还在,就能保住注册服务的可用性,只不过查到的
信息可能不是最新的,除此之外,Eureka还有一 种自我保护机制,如果在15分钟内超过85%的节点都没有正常的心跳,那么Eureka就认为客户端与注册中心出现了网络故障,此时会出现以下几种情况: 1. Eureka不再从注册列表中移除因为长时间没收到心跳而应该过期的服务 2. Eureka仍然能够接受新服务的注册和查询请求,但是不会被同步到其他节点上(即保证当前节点依然可用) 3. 当网络稳定时,当前实例新的注册信息会被同步到其他节点中
因此,Eureka可以很好的应对因网络故障导致部分节点失去联系的情况,而不会像zookeeper那样使整个注册服务瘫痪
ribbon
ribbon是什么
Spring Cloud Ribbon是基于Netlix Ribbon实现的一套客户端负载均衡的工具。
简单的说,Ribbon是Netflix发布的开源项目, 主要功能是提供客户端的软件负载均衡算法,将NetFlix的中间层服务连接在一起。Ribbon的客户端组件提供一系列完整的配置项如: 连接超时、重试等等。简单的说,就是在配置文件中列出LoadBalancer (简称LB:负载均衡)后面所有的机器,Ribbon会 自动的帮助你基于某种规则(如简单轮询,随机连接等等)去连接这些机器。我们也很容易使用Ribbon实现自定义的负载均衡算法!
ribbon能干嘛?
LB,即负载均衡(Load Balance) ,在微服务或分布式集群中经常用的-种应用。
负载均衡简单的说就是将用户的请求平摊的分配到多个服务上,从而达到系统的HA (高可用)。
常见的负载均衡软件有Nginx, Lvs等等
dubbo. SpringCloud中均给我们提供了负载均衡, SpringCloud的负载均衡算法可以自定义
负载均衡简单分类:
集中式LB
- 即在服务的消费方和提供方之间使用独立的LB设施,如Nginx, 由该设施负责把访问请求通过某种策 略转发至服务的提供方!
进程式LB
- 将LB逻辑集成到消费方,消费方从服务注册中心获知有哪些地址可用,然后自己再从这些地址中选出一个合适的服务器。
- ”Ribbon就属于进程内LB, 它只是一 个类库,集成于消费方进程,消费方通过它来获取到服务提供方的地址
使用
添加依赖(在消费方)
<!-- Ribbon的依赖-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-ribbon</artifactId>
<version>1.4.6.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<!-- Eureka依赖-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-netflix-eureka-client</artifactId>
</dependency>
配置
#Eureka配置
eureka:
client:
register-with-eureka: false #不向eureka注册自己
service-url:
#做集群需要关联集群的eureka服务器的地址,其实端口号都应该是7001,
#关联的只是服务器地址,这里因为只有一台电脑,就用了端口号代替
defaultZone: http://127.0.0.1:7001/eureka/,http://127.0.0.1:7002/eureka/,http://127.0.0.1:7003/eureka/
#常见错误
#参考文档博客园 https://www.cnblogs.com/cangqinglang/p/11704475.html
//负载均衡实现RestTemplate
@Bean
@LoadBalanced //Reibbon
public RestTemplate getRestTemplate(){
return new RestTemplate();
}
controller使用负载均衡
//Ribbon 我们这里的地址,应该是一个变量,通过服务名来访问
// private static final String REST_URL_PREFIX = "http://localhost:8001";
private static final String REST_URL_PREFIX = "http://SPRINGCLOUD-PROVIDER-DEPT";
启动
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableEurekaClient//启动
public class SpringCloudConsumer {
IRule接口
创建多个服务提供者
创建db02、db03数据库
CREATE DATABASE /*!32312 IF NOT EXISTS*/`db02` /*!40100 DEFAULT CHARACTER SET utf8 */;
USE `db02`;
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `dept`;
CREATE TABLE `dept` (
`dname` varchar(60) DEFAULT NULL,
`deptno` bigint(20) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`db_source` varchar(60) DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`deptno`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=11 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8 COMMENT='部门表';
insert into `dept`(`dname`,`deptno`,`db_source`) values ('开发部',1,'db02'),('人事部',2,'db02'),('财务部',3,'db02'),('市场部',4,'db02'),('运维部',5,'db02'),('klz',10,'db02');
CREATE DATABASE /*!32312 IF NOT EXISTS*/`db03` /*!40100 DEFAULT CHARACTER SET utf8 */;
USE `db03`;
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `dept`;
CREATE TABLE `dept` (
`dname` varchar(60) DEFAULT NULL,
`deptno` bigint(20) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`db_source` varchar(60) DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`deptno`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=11 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8 COMMENT='部门表';
insert into `dept`(`dname`,`deptno`,`db_source`) values ('开发部',1,'db03'),('人事部',2,'db03'),('财务部',3,'db03'),('市场部',4,'db03'),('运维部',5,'db03'),('klz',10,'db03');
创建服务提供者8002、8003
修改数据库和服务提供者id,端口号
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/db02?useUnicode=true&serverTimezone=GMT%2B8&characterEncoding=UTF-8&useSSL=false
instance-id: springcloud-provider-dept8002
port: 8002
但是服务名一定是一致的
application:
name: springcloud-provider-dept
测试
可以发现
SPRINGCLOUD-PROVIDER-DEPT n/a (3) (3) UP (3) - springcloud-provider-dept8001 , springcloud-provider-dept8003 , springcloud-provider-dept8002
启动客户端–使用者80
访问,可以发现数据是轮询的
http://localhost/consumer/dept/list
自定义分配算法
注意IRule接口,具有以下实现类
AbstractLoadBalancerRule 一般
AvailabilityFilleringRule 会先过滤掉,崩溃(跳闸)的服务,对剩下的进行轮询
BestAvailableRule
ClientConfigEnabledRoundRobinRule
PredicateBasedRule
RandomRule 随机
ResponseTimeWeightedRule
RetryRule 重试,会先按照轮询获取服务,如果服务获取失败,则会在指定的时间内进行重试
RoundRobinRule 轮询
WeightedResponseTimeRule 权重
ZoneAvoidanceRule
添加注解
//规则,轮询
@Bean
public IRule myRule(){
return new RandomRule();
}
自定义规则只需要实现IRule接口
FooConf iguration必须是@Configuration.但请注意,它不在主应用程序上下文的@ComponentScan中,否则将由所有@RibbonClients共享,如果您使用@ComponentScan (或@SpringBootApplication) .则需要采取措施避免包含({例如将其放在一 个单独的, 不重叠的包中,或者指定要在@ComponentScan) .
所以我们的自定义的类,不能放在启动类的目录下
Feign负载均衡
简介
feign是声明式的web service客户端,它让微服务之间的调用变得更简单了,类似controller调用service。 SpringCloud集成了Ribbon和Eureka,可在使用Feign时提供负载均衡的http客户端。只需要创建一一个接口,然后添加注解即可!feign,主要是社区,大家都习惯面向接口编程。这个是很多开发人员的规范。调用微服务访问两种方法
微服务名字[ribbon]
接口和注解[feign ]
Feign能干什么?
Feign旨在使编写Java Http客户端变得更容易
前面在使用Ribbon + RestTemplate时, 利用RestTemplate对Http请求的封装处理,形成了一套模板化的调用方法。但是在实际开发中,由于对服务依赖的调用可能不止- -处, 往往一个接口会被多处调用,所以通常都会针对每个微服务自行封装-些客户端类来包装这些依赖服务的调用。 所以,Feign在此基础 上做了进一步封装,由他来帮助我们定义和实现依赖服务接口的定义,在Feign的实现下,我们只需要创建一一个接口并使用注解的方式来配置它(类似于以前Dao接口上标注Mapper注解,现在是一个微服务接口上面标注一个Feign注解即可。)即可完成对服务提供方的接口绑定,简化了使用Spring Cloud Ribbon时,自动封装服务调用客户端的开发量。
Feign集成了Ribbon
利用Ribbon维护了MicroServiceCloud-Dept的服务列表信息,并且通过轮询实现了客户端的负载均衡,而与Ribbon不同的是,通过Feign只需要定义服务绑定接口且以声明式的方法,优雅而且简单的实现了服务调用。
使用
api添加service
//@Component
@FeignClient(value = "SPRINGCLOUD-PROVIDER-DEPT")
public interface DeptServiceFeign {
@GetMapping("/dept/get/{id}")
public Dept queryId(@PathVariable("id") Long id);
@GetMapping("/dept/list")
public List<Dept> queryAll();
@PostMapping("/dept/list")
public boolean addDept(Dept dept);
}
api 添加依赖
<!--Feign依赖-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-feign</artifactId>
<version>1.4.6.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
创建module:springcloud-comsumer-feign、
添加依赖
<!--Feign依赖-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-feign</artifactId>
<version>1.4.6.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
controller调用
@RestController
public class DeptController {
@Autowired
private DeptServiceFeign service =null;
@RequestMapping("/consumer/dept/get/{id}")
public Dept get(@PathVariable("id") Long id) {
return this.service.queryId(id);
}
@RequestMapping("/consumer/dept/add")
public boolean add(Dept dept) {
return this.service.addDept(dept);
}
@RequestMapping("/consumer/dept/list")
public List<Dept> list() {
return this.service.queryAll();
}
}
启用
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableEurekaClient//启动
@EnableFeignClients(basePackages = "com.mumulx")
public class SpringCloudConsumerFeign {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(SpringCloudConsumerFeign.class, args);
}
}
测试
启动7001、8001,feign
访问
http://localhost/consumer/dept/list
服务熔断
服务端
分布式系统面临的问题
复杂分布式体系结构中的应用程序有数十个依赖关系,每个依赖关系在某些时候将不可避免的失败!
服务雪崩
多个微服务之间调用的时候,假设微服务A调用微服务B和微服务C,微服务B和微服务C又调用其他的微服务,这就是所谓的”扇出”、如果扇出的链路上某个微服务的调用响应时间过长或者不可用,对微服务A的调用就会占用越来越多的系统资源,进而引起系统崩溃,所谓的“雪崩效应”。对于高流量的应用来说,单- -的后端依赖可能会导致所有服务器上的所有资源都在几秒中内饱和。比失败更糟糕的是,这些应用程序还可能导致服务之间的延迟增加,备份队列,线程和其他系统资源紧张,导致整个系统发生更多的级联故障,这些都表示需要对故障和延迟进行隔离和管理,以便单个依赖关系的失败,不能取消整个应用程序或系统。
我们需要:弃车保帅
什么是Hystrix
Hystrix是一个用于处理分 布式系统的延迟和容错的开源库,在分布式系统里,许多依赖不可避免的会调用失败,比如超时,异常等, Hystrix能够保证在一 个依赖出问题的情况下, 不会导致整体服务失败,避免级联故障,以提高分布式系统的弹性。
“断路器”本身是一种开关装置,当某个服务单元发生故障之后,通过断路器的故障监控(类似熔断保险丝),向调用方返回一个服务预期的,可处理的备选响应(FallBack) ,而不是长时间的等待或者抛出调用方法无法处理的异常,这样就可以保证了服务调用方的线程不会被长时间,不必要的占用,从而避免了故障在分布式系统中的蔓延,乃至雪崩
能干嘛
- 服务降级
- 服务熔断
- 服务限流
- 接近实时的监控
服务熔断
是什么
熔断机制是对应雪崩效应的一种微服务链路保护机制。当扇出链路的某个微服务不可用或者响应时间太长时,会进行服务的降级,进而熔断该节点微服务的调用,快速返回错误的响应信息。当检测到该节点微服务调用响应正常后恢复调用链路。在SpringCloud框架里熔断机制通过Hystrix实现。Hystrix会监控微服务间调用的状况, 当失败的调用到- -定阈值,缺省是5秒内20次调用失败就会启动熔断机制。熔断机制的注解是@HystrixCommand.
使用
添加依赖
<!-- hystrix依赖-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-hystrix</artifactId>
<version>1.4.6.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
@RestController
public class DeptController {
@Resource(name = "deptService")
private DeptServiceFeign deptService;
@HystrixCommand(fallbackMethod = "getHystrix")//指定备选方法
@GetMapping("/dept/get/{id}")
public Dept get(@PathVariable("id") Long id){
Dept dept = deptService.queryId(id);
if (dept == null) {
throw new RuntimeException("id=>" + id + ",不存在该用户,或信息无法找到");
}
return dept;
}
//备选方法
public Dept getHystrix(@PathVariable("id") Long id){
return new Dept().setDeptno(id).setDname("id=>"+id+",没有对应的信息,null~~").setDb_source("不存在该数据库");
}
}
@EnableEurekaClient//在服务启动后自动注册到eureka
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableDiscoveryClient//服务发现
@EnableCircuitBreaker//增加对熔断的支持
public class SpringCloudProvider8001 {
测试
启动7001,7002,8001-hystrix
服务降级
客户端
api提供降级
//降级
@Component
public class DeptServiceFeignFallbackFactory implements FallbackFactory {
@Override
public DeptServiceFeign create(Throwable throwable) {
// 谁失败了就返回谁
return new DeptServiceFeign() {
@Override
public Dept queryId(Long id) {
return new Dept()
.setDeptno(id)
.setDname("id=>"+id+"没有对应的信息,客户端提供了降级的信息,这个服务现在已经被关闭了")
.setDb_source("n没有数据");
}
@Override
public List<Dept> queryAll() {
return null;
}
@Override
public boolean addDept(Dept dept) {
return false;
}
};
}
}
指定关系
@FeignClient(value = "SPRINGCLOUD-PROVIDER-DEPT",fallbackFactory = DeptServiceFeignFallbackFactory.class)
public interface DeptServiceFeign {
feign开启
# 开启降级
feign:
hystrix:
enabled: true
测试
启动7001,7002,8001,feign
访问
http://localhost/consumer/dept/get/1
关闭8001
继续访问
{
deptno: 1,
dname: "id=>1没有对应的信息,客户端提供了降级的信息,这个服务现在已经被关闭了",
db_source: "n没有数据"
}
服务熔断:服务端某 个服务超时或者异常,引起熔脚,保险丝~
服务降级:客户端从整体网站请求负载考虑,当某个服务熔断或者关闭之后,服务将不再被调用此时在客户端,我们可以准备一个FallbackFactory,返回一个默认的值( 缺省值),整体的服务水平下降了但是,好歹能用
监控
客户端
添加依赖
<dependencies>
<!-- 我们需要拿到实体类,从api项目的pojo拿-->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.mumulx</groupId>
<artifactId>springcloud-api</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
</dependency>
<!-- junit-->
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- mysql依赖-->
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- druid数据源依赖-->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>druid</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- 日志核心依赖-->
<dependency>
<groupId>ch.qos.logback</groupId>
<artifactId>logback-core</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- springboot启动依赖-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis.spring.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- spirngboot测试依赖-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-test</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- springboot的web依赖-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- jetty依赖相当于tomcat(springboot自带tomcat)-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-jetty</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- 热部署依赖-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-devtools</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- eureka依赖-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-eureka</artifactId>
<version>1.4.6.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<!-- actutor完善监控信息(erekua的status指向网页的信息依赖)-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-actuator</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- Hystrix依赖-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-hystrix</artifactId>
<version>1.4.6.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<!-- Hystrix监控依赖-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-hystrix-dashboard</artifactId>
<version>1.4.6.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
springcloud-consumer-hystrix-dashboard
配置
server:
port: 9001
启动类
@SpringBootApplication(exclude= {DataSourceAutoConfiguration.class})
@EnableHystrixDashboard//开启监控
public class SpringCloudConsumerHystrixDashboard {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(SpringCloudConsumerHystrixDashboard.class,args);
}
}
服务提供者端添加依赖
(以将添加过了)
<!-- actutor完善监控信息(erekua的status指向网页的信息依赖)-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-actuator</artifactId>
</dependency>
测试
启动9001
访问
http://localhost:9001/hystrix
8001-hystrix
添加依赖
<!-- hystrix依赖-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-hystrix</artifactId>
<version>1.4.6.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
启动类添加配置
//增加一个servlet,将8001服务注册到dashboard流监控
@Bean
public ServletRegistrationBean getServlet() {
HystrixMetricsStreamServlet streamServlet = new HystrixMetricsStreamServlet();
ServletRegistrationBean registrationBean = new ServletRegistrationBean(streamServlet);
registrationBean.setLoadOnStartup(1);
registrationBean.addUrlMappings("/actuator/hystrix.stream");
registrationBean.setName("HystrixMetricsStreamServlet");
return registrationBean;
}
启动7001,8001-hystrix、9001
先访问
http://localhost:8001/dept/get/5
访问的方法必须是支持熔断的
即含有注解 @HystrixCommand(fallbackMethod = “getHystrix”)的
@HystrixCommand(fallbackMethod = "getHystrix")//指定备选方法
@GetMapping("/dept/get/{id}")
public Dept get(@PathVariable("id") Long id){
Dept dept = deptService.queryId(id);
if (dept == null) {
throw new RuntimeException("id=>" + id + ",不存在该用户,或信息无法找到");
}
return dept;
}
//备选方法
public Dept getHystrix(@PathVariable("id") Long id){
return new Dept().setDeptno(id).setDname("id=>"+id+",没有对应的信息,null~~").setDb_source("不存在该数据库");
}
在监控
http://localhost:8001/actuator/hystrix.stream
进入9001
添加监控
http://localhost:8001/actuator/hystrix.stream
Delay: 2000ms
Title: xxx
进入后进行监控
Zuul路由网关
概述
什么是Zuul?
Zuul包含了对请求的路由和过滤两个最主要的功能:
其中路由功能负责将外部请求转发到具体的微服务实例上,是实现外部访问统一入口的基础, 而过滤器功能则负责对请求的处理过程进行干预,是实现请求校验,服务聚合等功能的基础。Zuul和Eureka进行整合, 将Zuul自身注册为Eureka服务治理下的应用,同时从Eureka中获得其他微服务的消息,也即以后的访问微服务都是通过Zuul跳转后获得。
注意: Zuul服务最终还是会注册进Eureka
提供:代理+路由+过滤三大功能!
Zuul能干嘛?
- 路由
- 过滤
代码
新建module:springcloud-zuul-9527
添加依赖
<dependencies>
<!-- 我们需要拿到实体类,从api项目的pojo拿-->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.mumulx</groupId>
<artifactId>springcloud-api</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
</dependency>
<!-- springboot的web依赖-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- jetty依赖相当于tomcat(springboot自带tomcat)-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-jetty</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- 热部署依赖-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-devtools</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- actutor完善监控信息(erekua的status指向网页的信息依赖)-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-actuator</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- Ribbon的依赖-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-ribbon</artifactId>
<version>1.4.6.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<!-- Hystrix依赖-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-hystrix</artifactId>
<version>1.4.6.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.reactivestreams</groupId>
<artifactId>reactive-streams</artifactId>
<version>1.0.3</version>
</dependency>
<!-- Hystrix监控依赖-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-hystrix-dashboard</artifactId>
<version>1.4.6.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<!-- Eureka依赖-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-eureka</artifactId>
<version>1.4.6.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<!-- Zuul依赖-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-zuul</artifactId>
<version>1.4.6.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
配置
server:
port: 9527
spring:
application:
name: springCloud-zuul
#Eureka的配置,服务注册到哪里
eureka:
client:
service-url:
defaultZone: http://localhost:7001/eureka/,http://localhost:7002/eureka/,http://localhost:7003/eureka/
instance:
instance-id: springcloud-zuul-9527
prefer-ip-address: true
#info配置
info:
app.name: mumulx-springcloud
company.name: com.mumulx
开启
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableZuulProxy
public class SpringCloudZuul9527 {
public static void main(String[] args)
本地添加网关,C:\Windows\System32\drivers\etc\hosts文件
127.0.0.1 www.mywin10.com
测试:
启动7001,8001-hystrix,9527
访问
方式一
http://localhost:8001/dept/get/5
方式二
http://www.mywin10.com:9527/springcloud-provider-dept/dept/get/2
这样就把真实的地址隐藏起来了
但是这样暴漏了微服务的名称springcloud-provider-dept
配置zuul
增加9527配置
# zuul配置
zuul:
routes:
mydept.serviceId: springcloud-provider-dept
mydept.path: /mydept/** #将服务名改一个名字代替服务名
ignored-services: springcloud-provider-dept #忽略服务名,不能用服务名访问了,否则报500
prefix: #设置公共前缀
访问
http://www.mywin10.com:9527/mydept/dept/get/2
这样就隐藏了ip和微服务的名称
SpringCloud config分布式配置
概述
分布式系统面临的-配置文件的问题
微服务意味着要将单体应用中的业务拆分成一个个子服务,每个服务的粒度相对较小,因此系统中会出现大量的服务,由于每个服务都需要必要的配置信息才能运行,所以一套集中式的, 动态的配置管理设施是必不可少的。SpringCloud提供了ConfigServer来解决这个问题,我们每一个微服务自 己带着- -个application.yml, 那上百的的配置文件要修改起来,岂不是要发疯!
什么是SpringCloud config分布式配置中心
可以将配置文件放在本地git仓库,也可以放在远程git仓库
Spring Cloud Config为微服务架构中的微服务提供集中化的外部配置支持,配置服务器为各个不同微服务应用的所有环节提供了一个中心化的外部配置。
Spring Cloud Config 分为服务端和客户端两部分;
服务端也称为分布式配置中心,它是一 个独立的微服务应用,用来连接配置服务器并为客户端提供获取配置信息,加密,解密信息等访问接口。
客户端则是通过指定的配置中心来管理应用资源,以及与业务相关的配置内容,并在启动的时候从配置中心获取和加载配置信息。配置服务器默认采用git来存储配置信息,这样就有助于对环境配置进行版本管理。并且可以通过git客户端工具来方便的管理和访问配置内容.
SpringCloud config分布式配置中心能干嘛
集中管理配置文件
不同环境,不同配置,动态化的配置更新,分环境部署,比如/dev /test/ /prod /beta /release
运行期间动态调整配置,不再需要在每个服务部署的机器上编写配置文件,服务会向配置中心统-拉取配置自己的信息。
当配置发生变动时,服务不需要重启,即可感知到配置的变化,并应用新的配置
将配置信息以REST接口的形式暴露
SpringCloud config分布式配置中心与github整合
由于Spring Cloud Config默认使用Git来存储配置文件(也有其他方式,比如支持SVN和本地文件),但是最推荐的还是Git,而且使用的是http / https访问的形式;
使用
服务端
git新建仓库springCloud-config
新建spring配置文件application.yml
spring:
profiles:
active: dev
---
#spring的配置
spring:
profiles: dev
application:
name: springcloud-config-dev
---
#spring的配置
spring:
profiles: test
application:
name: springcloud-config-test
创建新module:springcloud-config-service-3344
添加依赖
<dependencies>
<!-- web-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!--config-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-config-server</artifactId>
<version>2.1.1.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<!-- actuator完善页面监控依赖-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-actuator</artifactId>
<version>2.1.11.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
配置
server:
port: 3344
spring:
application:
name: springcloud-config-server-3344
#连接远端仓库
cloud:
config:
server:
git:
uri: https://github.com/mumulx/springCloud-config.git #是http,不是ssh
启用
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableConfigServer
public class SpringCloudConfigServer3344 {
测试
启动3344
测试
访问的三种方式
http://localhost:3344/application-dev.yml
http://localhost:3344/application/test/master
http://localhost:3344/master/application-dev.yml
客户端
客户端去 请求服务端获取配置
仓库新建config-server.yml
spring:
profiles:
active: dev
---
server:
port: 8201
#spring的配置
spring:
profiles: dev
application:
name: springcloud-provider-dept
#Eureka的配置,服务注册在哪里
eureka:
client:
service-url:
defaultZone: http://localhost:7002/eureka/,http://127.0.0.1:7003/eureka/
---
server:
port: 8202
#spring的配置
spring:
profiles: test
application:
name: springcloud-provider-dept
#Eureka的配置,服务注册在哪里
eureka:
client:
service-url:
defaultZone: http://localhost:7002/eureka/,http://127.0.0.1:7003/eureka/
git push
新建module:springcloud-config-client-3355
添加依赖
<dependencies>
<!-- web-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!--config-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-config</artifactId>
<version>2.1.1.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<!-- actuator完善页面监控依赖-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-actuator</artifactId>
<version>2.1.11.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
bootstrap.yml与application.yml
配置
bootstrap.yml
#系统级别的配置(高于用户级别的配置)
#只能识别application.yml和boostrap.yml,别的名字不能识别
spring:
cloud:
config:
#springcloud-config采用的是sv(服务器客户端)的架构模式
#服务器(3344)连gitee,客户端(3355)连服务器
uri: http://localhost:3344 #服务器地址
name: config-client #需要从gitee上读取的资源名称
profile: dev #开发模式 test是测试模式
label: master #geitee的分支
application.yml
#用户级别的配置
spring:
application:
name: springcloud-config-client-3355
编写controller获取配置信息ConfigClientController
@RestController
public class ConfigClientController {
@Value("${spring.application.name}")
private String applicationName;
@Value("${eureka.client.service-url.defaultZone}")
private String eurekaServer;
@Value("${server.port}")
private String port;
@RequestMapping("/config")
public String getConfig() {
return "applicationName:"+applicationName+
"eurekaServer:"+eurekaServer+
"port:"+port;
}
}
测试
启动3344,3355
测试3344能获取配置
http://localhost:3344/master/config-client-dev.yml
访问
http://localhost:8201/config
获取配置信息,此时我们发现我们并没有配置8201的端口,但是客户端却是通过8201进行访问的
使用springCloud-config将之前的模块优化
新建配置文件config-eureka.yml、config-dept.yml
config-eureka.yml
spring:
profiles:
active: dev
---
server:
port: 7001
#spring的配置
spring:
profiles: dev
application:
name: springcloud-config-eureka
#eureka配置
eureka:
instance:
hostname: localhost #Eureka服务端的实例名称,localhost代表服务器的地址,最后要换的
client:
register-with-eureka: false #表示是否向eureka注册中心注册自己
fetch-registry: false #fetch-registry如果为false, 则表示自己为注册中心
service-url: # 监控页面
#单机不做集群defaultZone: http://${eureka.instance.hostname}:${server.port}/eureka/
#localhost代表服务器的地址,最后要换的 ,集群互相关联7001关联7002和7003
#其实用的端口号都应该是7001,关联的是不同服务器的地址,因为我只有一个电脑,就用了端口号代替
defaultZone: http://localhost:7002/eureka/,http://127.0.0.1:7003/eureka/
---
server:
port: 7001
#spring的配置
spring:
profiles: test
application:
name: springcloud-config-eureka
#eureka配置
eureka:
instance:
hostname: localhost #Eureka服务端的实例名称,localhost代表服务器的地址,最后要换的
client:
register-with-eureka: false #表示是否向eureka注册中心注册自己
fetch-registry: false #fetch-registry如果为false, 则表示自己为注册中心
service-url: # 监控页面
#单机不做集群defaultZone: http://${eureka.instance.hostname}:${server.port}/eureka/
#localhost代表服务器的地址,最后要换的 ,集群互相关联7001关联7002和7003
#其实用的端口号都应该是7001,关联的是不同服务器的地址,因为我只有一个电脑,就用了端口号代替
defaultZone: http://localhost:7002/eureka/,http://127.0.0.1:7003/eureka/
config-dept.yml
spring:
profiles:
active: dev
---
Server:
port: 8001
mybatis:
# 指定全局配置文件位置
config-location: classpath:mybatis/mybatis-config.xml
# 指定sql映射文件位置
mapper-locations: classpath:mybatis/mapper/*.xml
# 指定实体类
type-aliases-package: com.mumulx.entity
spring:
profiles: dev
application:
name: springcloud-config-eureka
datasource:
# 数据源基本配置
username: root
password: 135451
driver-class-name: org.gjt.mm.mysql.Driver
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/db01?useUnicode=true&serverTimezone=GMT%2B8&characterEncoding=UTF-8&useSSL=false
type: com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource
#Eureka的配置,服务注册到哪里
eureka:
client:
service-url:
defaultZone: http://localhost:7001/eureka/,http://localhost:7002/eureka/,http://localhost:7003/eureka/
instance:
instance-id: springcloud-provider-dept8001
prefer-ip-address: true #true,显示服务的ip地址
#info配置
info:
app.name: mumulx-springcloud
company.name: com.mumulx
---
Server:
port: 8001
mybatis:
# 指定全局配置文件位置
config-location: classpath:mybatis/mybatis-config.xml
# 指定sql映射文件位置
mapper-locations: classpath:mybatis/mapper/*.xml
# 指定实体类
type-aliases-package: com.mumulx.entity
spring:
profiles: test
application:
name: springcloud-config-eureka
datasource:
# 数据源基本配置
username: root
password: 135451
driver-class-name: org.gjt.mm.mysql.Driver
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/db01?useUnicode=true&serverTimezone=GMT%2B8&characterEncoding=UTF-8&useSSL=false
type: com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource
#Eureka的配置,服务注册到哪里
eureka:
client:
service-url:
defaultZone: http://localhost:7001/eureka/,http://localhost:7002/eureka/,http://localhost:7003/eureka/
instance:
instance-id: springcloud-provider-dept8001
prefer-ip-address: true #true,显示服务的ip地址
#info配置
info:
app.name: mumulx-springcloud
company.name: com.mumulx
新建module:springcloud-config-eureka-7001
将7001全部复制到config-7001
导包
<!--config-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-config</artifactId>
<version>2.1.1.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
新建bootstrap.yml
#系统级别的配置(高于用户级别的配置)
#只能识别application.yml和boostrap.yml,别的名字不能识别
spring:
cloud:
config:
#springcloud-config采用的是sv(服务器客户端)的架构模式
#服务器(3344)连gitee,客户端(3355)连服务器
uri: http://localhost:3344 #服务器地址
name: config-eureka #需要从gitee上读取的资源名称
profile: dev #开发模式 test是测试模式
label: master #geitee的分支
application.yml
spring:
application:
name: springcloud-config-eureka-7001
测试
启动3344
测试
http://localhost:3344/master/config-eureka-dev.yml
可以获取eureka的配置信息
启动config-7001
测试
http://localhost:7001/
新建module:springcloud-config-provider-8001
将8001复制到config-8001
导包
<!--config-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-config</artifactId>
<version>2.1.1.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
配置
bootstrap.yml
#系统级别的配置(高于用户级别的配置)
#只能识别application.yml和boostrap.yml,别的名字不能识别
spring:
cloud:
config:
#springcloud-config采用的是sv(服务器客户端)的架构模式
#服务器(3344)连gitee,客户端(3355)连服务器
uri: http://localhost:3344 #服务器地址
name: config-dept #需要从gitee上读取的资源名称
profile: dev #开发模式 test是测试模式
label: master #geitee的分支
application.yml
spring:
application:
name: springcloud-config-provider-dept-8001
测试
启动3344
http://localhost:3344/master/config-dept-dev.yml
启动config-7001,config-8001
查看是否注册进来
http://localhost:7001/
是否可以使用



