Mybatis
简介
mybatis:
ibatis:apache
2010 ibatis-> google colde ,Mybatis
MyBatis可以简化JDBC操作,实现数据的持久化 。
ORM:Object Relational Mapping
ORM可以解决数据库与程序间的异构性,比如在Java中我们使用String表示字符串,而Oracle中可使用varchar2,MySQL中可使用varchar,SQLServer可使用nvarchar。
对象关系映射(英语:Object Relational Mapping,简称ORM,或O/RM,或O/R mapping),用于实现面向对象编程语言里不同类型系统的数据之间的转换。简单的说,ORM是通过使用描述对象和数据库之间映射的元数据,将程序中的对象与关系数据库相互映射。
person对象 person表 之间一一映射起来
ORM:概念 ,Mybatis是ORM的一个实现/Hibernate orm可以是的开发人员像操作对象一样操作数据库表。
开发mybatis程序从步骤:
所有学习源码git地址
jar包
mybatis-3.4.6.jar
类–表
public class Student {
private int id;
private String name;
private int age ;
public Student() {
}
public Student(int id, String name, int age) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return this.id+","+this.name+","+this.age ;
}
}
配置mybatis
conf.xml:配置数据库信息 和 需要加载的映射文件 表 - 类
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE configuration
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd">
<configuration>
<environments default="development">
<environment id="development">
<transactionManager type="JDBC"/>
<dataSource type="POOLED">
<!-- 配置数据库信息 -->
<property name="driver" value="oracle.jdbc.OracleDriver"/>
<property name="url" value="jdbc:oracle:thin:@127.0.0.1:1521:ORCL"/>
<property name="username" value="scott"/>
<property name="password" value="tiger"/>
</dataSource>
</environment>
</environments>
<mappers>
<!-- 加载映射文件 -->
<mapper resource="org/lanqiao/entity/personMapper.xml"/>
</mappers>
</configuration>
映射文件xxMapper.xml :增删改查标签
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="org.lanqiao.entity.personMapper">
<select id="queryPersonById" resultType="org.lanqiao.entity.Person" parameterType="int">
select * from person where id = #{id}
</select>
</mapper>
测试类:
public class TestMyBatis {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//加载MyBatis配置文件(为了访问数据库)
Reader reader = Resources.getResourceAsReader("conf.xml") ;
SqlSessionFactory sessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(reader) ;
//session - connection
SqlSession session = sessionFactory.openSession() ;
String statement = "org.lanqiao.entity.personMapper.queryPersonById" ;
Student person = session.selectOne( statement,1 ) ;
System.out.println(person);
session.close();
}
}
session.selectOne(“需要查询的SQL的namespace.id”,“SQL的参数值”);
conf.xml配置文件
配置文件的提示功能是通过
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd"
来配置的,因此需要联网,也可以将http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd下载下来,通过,windows-Preferences–>XML–>XML Catalog–>Catalog Entry指定文件的内容;其中Location放文件地址,Key放-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN
切换环境
<!-- 通过environments的default值 和 environment的 id 来指定 MyBatis运行时的数据库环境-->
<environments default="development">
<!-- 开发环境(自己的计算机) -->
<environment id="development">
<!-- 事务提交方式:
JDBC:利用JDBC方式处理事务(手工commit rollback close)
MANAGED:将事务交由 其他组件去托管(spring ,jobss),默认 会关闭连接。
关闭默认值,默认不关闭
<transactionManager type="MANAGED"/>
<property name="closeConnection" value="false"/>
-->
<transactionManager type="JDBC" />
<!-- 数据源类型:
UNPOOLED:传统的JDBC模式(每次访问数据库,均需要 打开、关闭等数据库操作,但是 打开、关闭数据库是比较消耗性能的,不推荐使用)
POOLED:使用数据库连接池
JNDI:从tomcat中获取一个内置的数据库连接池 (数据库连接池-数据源 )
-->
<dataSource type="POOLED">
<!-- 配置数据库信息 -->
<property name="driver" value="oracle.jdbc.OracleDriver"/>
<property name="url" value="jdbc:oracle:thin:@127.0.0.1:1521:ORCL"/>
<property name="username" value="scott"/>
<property name="password" value="tiger"/>
</dataSource>
</environment>
<!-- 真正的项目应该在 发布的那台计算机上运行 -->
<environment id="shishi">
<transactionManager type="JDBC"/>
<dataSource type="POOLED">
<!-- 配置数据库信息 -->
<property name="driver" value="oracle.jdbc.OracleDriver"/>
<property name="url" value="jdbc:oracle:thin:@192.168.1.183:1521:ORCL"/>
<property name="username" value="scott"/>
<property name="password" value="tiger"/>
</dataSource>
</environment>
<!-- -->
<environment id="test">
<transactionManager type="JDBC"/>
<dataSource type="POOLED">
<!-- 配置数据库信息 -->
<property name="driver" value="oracle.jdbc.OracleDriver"/>
<property name="url" value="jdbc:oracle:thin:@192.168.1.111:1521:ORCL"/>
<property name="username" value="scott"/>
<property name="password" value="tiger"/>
</dataSource>
</environment>
</environments>
还可以通过硬编码的方式指定环境,即使conf中default已经指定了默认环境。可以通过build的第二参数 指定数据库环境
SqlSessionFactory sessionFacotry = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(reader, "development");
xxxMapper.xml文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<!-- namespace:该mapper.xml映射文件的 唯一标识 -->
<mapper namespace="org.lanqiao.mapper.StudentMapper">
</mapper>
后续通过 namespace.id定位sql语句
parameterType:输入参数的类型
resultType:查询返回结果值的类型 ,返回类型
复习第一个MyBatis程序:
mybatis.jar ojdbc.jar
conf.xml (数据库配置信息、映射文件)
表-类:映射文件 mapper.xml
测试
基础方式的增删改查CRUD:
mybatis约定:
输入参数parameterType 和 输出参数resultType ,在形式上都只能有一个
如果输入/输出参数 :
是简单类型(8个基本类型+String) 是可以使用任何占位符,#{xxxx}
如果是对象类型,则必须是对象的属性 #{属性名}
输出参数:
- 如果返回值类型是一个 对象(如Student),则无论返回一个、还是多个,在resultType都写成
org.lx.entity.Student即resultType="org.lx.entity.Student"
- 如果返回值类型是一个 对象(如Student),则无论返回一个、还是多个,在resultType都写成
注意事项:
如果使用的 事务方式为 jdbc,则需要 手工commit提交,即
session.commit();所有的标签
<select><update>等 ,都必须有sql语句,但是sql参数值可选(重载了函数,有一个参数,有两个参数)sql有参数:session.insert(statement, 参数值 ); sql没参数:session.insert(statement);
增加
<insert id="addStudent" parameterType="org.lanqiao.entity.Student" >
insert into student(stuno,stuname,stuage,graname) values(#{stuNo},#{stuName},#{stuAge},#{graName} )
</insert>
String statement = "org.lanqiao.entity.studentMapper."+"addStudent";
Student student = new Student(13, "ww3", 23, "s3");
int count = session.insert(statement,student);
session.commit();
删除
<delete id="deleteStudentByStuno" parameterType="int">
delete from student where stuno = #{stuno}
</delete>
String statement = "org.lanqiao.entity.studentMapper."+"deleteStudentByStuno";
int count = session.delete(statement,3)
session.commit();
修改
<update id="updateStudentByStuno" parameterType="org.lx.entity.Student" >
update student set stuname=#{stuName} ,stuage=#{stuAge},graname=#{graName} where stuno=#{stuNo}
</update>
String statement = "org.lanqiao.entity.studentMapper."+"updateStudentByStuno";
Student student = new Student();
// 修改哪个人,where stuno =2
student.setStuNo(2);
// 修改成什么样子?
student.setStuName("ls");
student.setStuAge(24);
student.setGraName("s1");
int count = session.update(statement,student)
session.commit();
查询
查询一个
<select id="queryStudentByStuno" parameterType="int" resultMap="org.lx.entity.Student" >
select * from student where stuno = #{stuno}
</select>
String statement = "org.lanqiao.entity.studentMapper."+"queryStudentByStuno";
Student student = session.selectOne(statement,1)
查询多个
<select id="queryAllStudents" resultType="org.lx.entity.Student" >
select * from student
</select>
String statement = "org.lanqiao.entity.studentMapper."+"queryAllStudents";
List<Student> students = session.selectList(statement)
mapper动态代理方式的crud (MyBatis接口开发):
原则:约定优于配置
硬编码方式
abc.java
Configuration conf = new Configuration();
con.setName("myProject") ;
配置方式:
abc.xml
<name>myProject</name>
配置方式优于硬编码方式
约定方式优于硬编码方式
约定:
默认值就是myProject
具体实现的步骤:
基础环境:
mybatis.jar/ojdbc.jar、conf.xml、mapper.xml
不同之处
约定的目标:省略掉statement,即根据约定直接可以定位出SQL语句
接口,接口中的方法必须遵循以下约定:
方法名和mapper.xml文件中标签的id值相同
方法的 输入参数和mapper.xml文件中标签的 parameterType类型一致 (如果mapper.xml的标签中没有 parameterType,则说明方法没有输入参数)
方法的返回值和mapper.xml文件中标签的 resultType类型一致 (无论查询结果是一个 还是多个(student、
List<Student>),在mapper.xml标签中的resultType中只写 一个(Student);如果没有resultType,则说明方法的返回值为void)
除了以上约定,要实现 接口中的方法 和 Mapper.xml中SQL标签一一对应,还需要以下1点:
namespace的值 ,就是 接口的全类名( 接口 - mapper.xml 一一对应)
匹配的过程:(约定的过程)
- 根据 接口名 找到 mapper.xml文件(根据的是namespace=接口全类名)
根据 接口的方法名 找到 mapper.xml文件中的SQL标签 (方法名=SQL标签Id值)
以上2点可以保证: 当我们调用接口中的方法时, 程序能自动定位到 某一个Mapper.xml文件中的sqL标签
习惯:SQL映射文件(mapper.xml) 和 接口放在同一个包中 (注意修改conf.xml中加载mapper.xml文件的路径)
以上,可以通过接口的方法->SQL语句
接口中的方法->SQL语句
执行:
通过session对象获取接口(session.getMapper(接口.class);),再调用该接口中的方法,程序会自动执行该方法对应的SQL。
增加
<insert id="addStudent" parameterType="org.lanqiao.entity.Student" >
insert into student(stuno,stuname,stuage,graname) values(#{stuNo},#{stuName},#{stuAge},#{graName} )
</insert>
void addStudent(Student student);
Student student = new Student(13, "ww3", 23, "s3");
StudentMapper studentMapper = session.getMapper(StudentMapper.class);
studentMapper.addStudent(student);
删除
<delete id="deleteStudentByStuno" parameterType="int">
delete from student where stuno = #{stuno}
</delete>
void deleteStudentByStuno(int stuno);
StudentMapper studentMapper = session.getMapper(StudentMapper.class);
studentMapper.deleteStudentByStuno(13);
修改
<update id="updateStudentByStuno" parameterType="org.lx.entity.Student" >
update student set stuname=#{stuName} ,stuage=#{stuAge},graname=#{graName} where stuno=#{stuNo}
</update>
void updateStudentByStuno(Student student);
// 修改的参数
Student student = new Student();
// 修改哪个人,where stuno =2
student.setStuNo(2);
// 修改成什么样子?
student.setStuName("ls");
student.setStuAge(24);
student.setGraName("s1");
// 执行
StudentMapper studentMapper = session.getMapper(StudentMapper.class);
studentMapper.updateStudentByStuno(student);
查询
查询单个学生
<select id="queryStudentByStuno" parameterType="int" resultType="org.lanqiao.entity.Student" >
select * from student where stuno = #{stuno}
</select>
Student queryStudentByStuno(int stuno);
StudentMapper studentMapper = session.getMapper(StudentMapper.class);
Student student = studentMapper.queryStudentByStuno
查询多个
<select id="queryAllStudents" resultType="org.lanqiao.entity.Student" >
select * from student
</select>
List<Student> queryAllStudents();
StudentMapper studentMapper = session.getMapper(StudentMapper.class);
List<Student> students = studentMapper.queryAllStudents();// 接口的方法->SQL
优化、
可以将配置信息 单独放入 db.properties文件中,然后再动态引入
新建文件db.properties
driver=oracle.jdbc.OracleDriver
url=jdbc:oracle:thin:@127.0.0.1:1521:ORCL
username=scott
password=tiger
配置
<configuration>
<properties resource="db.properties"/>
使用
<environment id="development">
<transactionManager type="JDBC" />
<dataSource type="POOLED">
<!-- 配置数据库信息 -->
<property name="driver" value="${driver}" />
<property name="url" value="${url}" />
<property name="username" value="${username}" />
<property name="password" value="${password}" />
</dataSource>
</environment>
引入之后,使用${key}
MyBatis全局参数
Mybatis全局参数.png
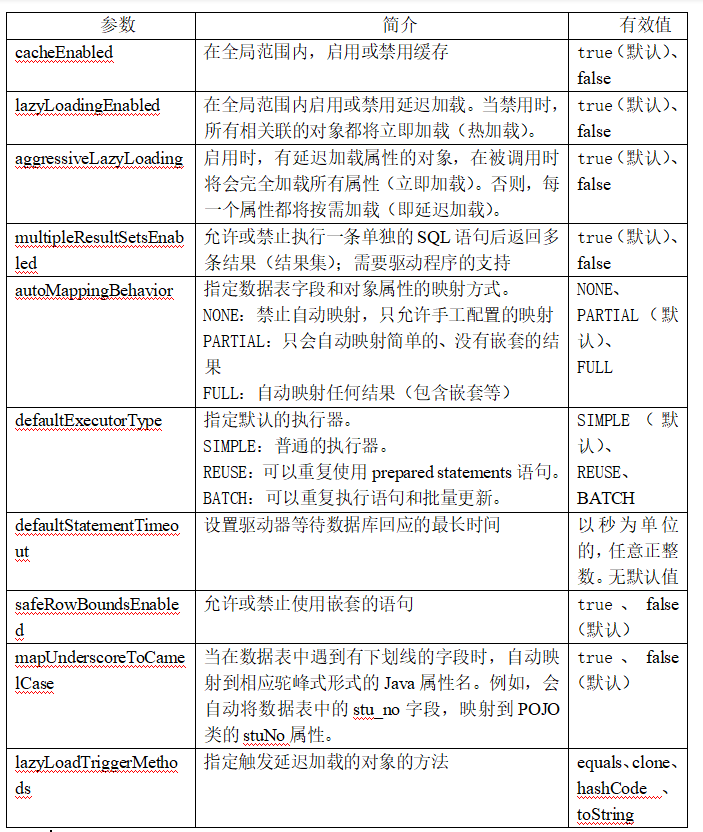
了解即可
在conf.xml中设置,在configuration里面
<settings>
<setting name="cacheEnabled" value="false" />
<setting name="lazyLoadingEnabled" value="false" />
</settings>
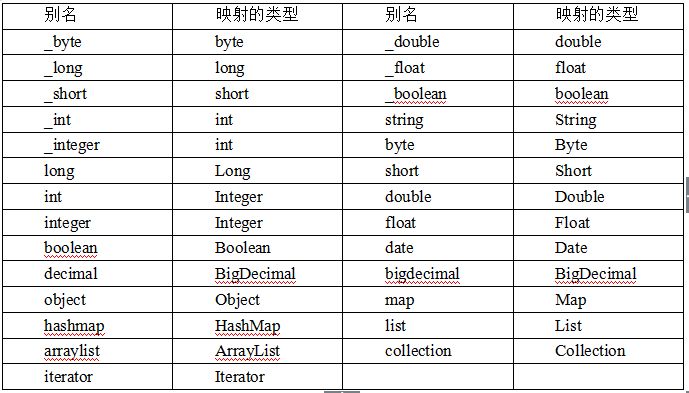
别名 conf.xml
设置单个别名
<!-- 设置单个/多个别名 --> <typeAliases> <!-- 单个别名 (别名 忽略大小写) --> <typeAlias type="org.lanqiao.entity.Student" alias="student"/> </typeAliases>使用,在xxMapper.xml中
<select id="queryAllStudents" resultType="sTuDenT" > select * from student </select>别名,忽略大小写
批量设置别名
<typeAliases> <!-- 批量定义别名 (别名 忽略大小写),以下会自动将该包中的所有类 批量定义别名: 别名就是类名(不带包名,忽略大小写) --> <package name="org.lanqiao.entity"/> </typeAliases>别名,忽略大小写
除了自定义别名外,MyBatis还内置了一些常见类的别名。
类型处理器(类型转换器)
MyBatis自带一些常见的类型处理器
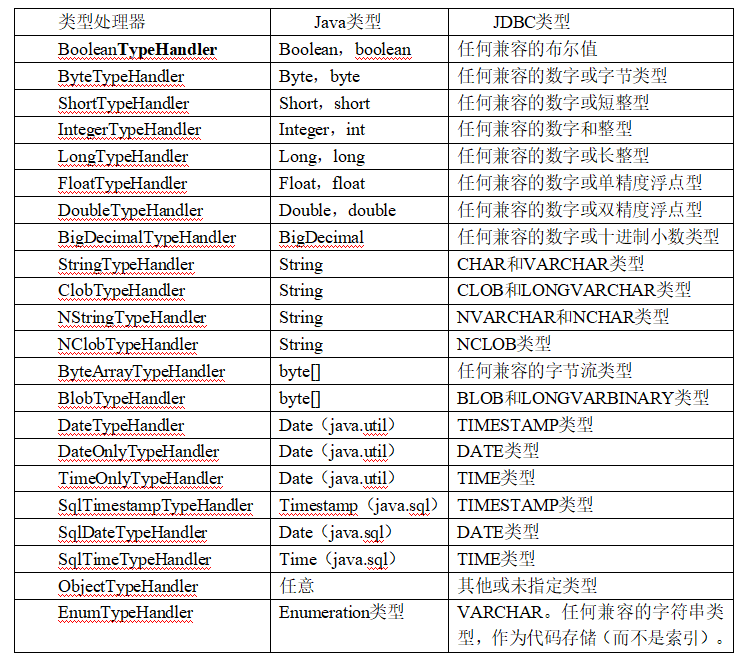
自定义MyBatis类型处理器
java -数据库(jdbc类型)
示例:
实体类Student : boolean stuSex
true:男
false:女
表student: number stuSex
1:男
0:女
自定义类型转换器(boolean -number)步骤:
创建转换器:需要实现TypeHandler接口
通过阅读源码发现,此接口有一个实现类 BaseTypeHandler ,因此 要实现转换器有2种选择:
- 实现接口TypeHandler接口
继承BaseTypeHandler
//BaseTypeHandler<java类型> public class BooleanAndIntConverter extends BaseTypeHandler<Boolean>{ //java(boolean)-DB(number) /* * ps:PreparedStatement对象 * i:PreparedStatement对象操作参数的位置 * parameter:java值 * jdbcType:JDBC操作的数据库类型 */ @Override public void setNonNullParameter(PreparedStatement ps, int i, Boolean parameter, JdbcType jdbcType) throws SQLException { if(parameter) { //1 ps.setInt(i, 1); }else { // 0 ps.setInt(i, 0); } } //db(number)->java(boolean) @Override public Boolean getNullableResult(ResultSet rs, String columnName) throws SQLException { int sexNum = rs.getInt(columnName) ;//rs.getInt("stuno") ; // if(sexNum == 1) // // return true; // else { // return false ; // } return sexNum == 1?true:false ; } @Override public Boolean getNullableResult(ResultSet rs, int columnIndex) throws SQLException { int sexNum = rs.getInt(columnIndex) ;//rs.getInt(1) return sexNum == 1?true:false ; } @Override public Boolean getNullableResult(CallableStatement cs, int columnIndex) throws SQLException { int sexNum = cs.getInt(columnIndex) ;//rs.getInt(1) return sexNum == 1?true:false ; } }
配置conf.xml
<typeHandlers> <typeHandler handler="org.lanqiao.converter.BooleanAndIntConverter" javaType="Boolean" jdbcType="INTEGER" /> </typeHandlers>使用
查询
<!-- 查询:使用了类型转换器 1如果 类中属性 和表中的字段 类型能够合理识别 (String-varchar2),则可以使用resultType;否则(boolean-number) 使用resultMap 2如果 类中属性名 和表中的字段名能够合理识别 (stuNo -stuno)则可以使用resultType;否则(id-stuno) 使用resultMap --> <select id="queryStudentByStunoWithConverter" parameterType="int" resultMap="studentResult" > select * from student where stuno = #{stuno} </select><resultMap type="student" id="studentResult"> <!-- 分为主键id 和非主键 result--> <id property="stuNo" column="stuno" /> <result property="stuName" column="stuname" /> <result property="stuAge" column="stuage" /> <result property="graName" column="graname" /> <result property="stuSex" column="stusex" javaType="boolean" jdbcType="INTEGER"/> </resultMap>注意#{stuNo} 中存放的是 属性值,需要严格区分大小写。
resultMap可以实现2个功能:
类型转换
属性-字段的映射关系
<resultMap type="student" id="studentMapping"> <!-- 分为主键id 和非主键 result--> <id property="id" column="stuno" /> <result property="stuName" column="stuname" /> <result property="stuAge" column="stuage" /> <result property="graName" column="graname" /> <result property="stuSex" column="stusex" javaType="boolean" jdbcType="INTEGER"/> </resultMap>当表中的字段名和类中的属性名不同是,也可以通过resultMap进行转换
Student queryStudentByStunoWithConverter(int stuno);StudentMapper studentMapper = session.getMapper(StudentMapper.class); Student student = studentMapper.queryStudentByStunoWithConverter(1);// 接口中的方法->SQL语句
需要注意的问题: INTEGER
查询:使用了类型转换器
如果 类中属性 和表中的字段 类型能够合理识别 (String-varchar2),则可以使用resultType;否则(boolean-number) 使用resultMap
如果 类中属性名 和表中的字段名能够合理识别 (stuNo -stuno)则可以使用resultType;否则(id-stuno) 使用resultMap
增加
<!-- 带转换器的增加 --> <insert id="addStudentWithConverter" parameterType="student" > insert into student(stuno,stuname,stuage,graname,stusex) values(#{stuNo},#{stuName},#{stuAge},#{graName} ,#{stuSex ,javaType=boolean ,jdbcType=INTEGER } ) </insert>//增加 void addStudentWithConverter(Student student);Student student = new Student(63, "ww53", 23, "s3"); student.setStuSex(true);// 1 StudentMapper studentMapper = session.getMapper(StudentMapper.class); studentMapper.addStudentWithConverter(student); session.commit(); // 提交事务
输入参数:parameterType
类型为 简单类型(8个基本类型+String)
#{}、${}的区别
存放的值不同
#{任意值},一般建议不要乱写,即见名知意 ${value} ,其中的标识符只能是value输出不同
#{}自动给String类型加上'' (自动类型转换) ${} 原样输出,但是适合于 动态排序(动态字段) select stuno,stuname,stuage from student where stuname = #{value} select stuno,stuname,stuage from student where stuname = '${value}'动态排序:
<select id="queryStudentOrderByColumn" parameterType="string" resultType="student" > select stuno,stuname,stuage from student order by ${value} asc </select>List<Student> queryStudentOrderByColumn(String column);StudentMapper studentMapper = session.getMapper( StudentMapper.class) ; List<Student> students = studentMapper.queryStudentOrderByColumn("stuno") ;//接口的方法->SQLSQL注入
#{}可以防止SQL注入
${}不防止
什么是SQL注入
SQL注入是通过把SQL命令插入到web表单提交或通过页面请求的查询字符串,最终达到欺骗服务器执行恶意的SQL指令。注入攻击的本质是把用户输入的数据当做代码执行。
举例如: 表单有两个用户需要填写的表单数据,用户名和密码,如果用户输入admin(用户名),111(密码),若数据库中存在此用户则登录成功。SQL大概是这样
SELECT * FROM XXX WHERE userName = admin and password = 111但若是遭到了SQL注入,输入的数据变为 admin or 1 =1 # 密码随便输入,这时候就直接登录了,SQL大概是这样
SELECT * FROM XXX WHERE userName = admin or 1 = 1 # and password = 111,因为 # 在sql语句中是注释,将后面密码的验证去掉了,而前面的条件中1 = 1始终成立,所以不管密码正确与否,都能登录成功。
mybatis中的#{} 为什么能防止sql注入,${}不能防止sql注入
答: #{}在mybatis中的底层是运用了PreparedStatement 预编译,传入的参数会以 ? 形式显示,因为sql的输入只有在sql编译的时候起作用,当sql预编译完后,传入的参数就仅仅是参数,不会参与sql语句的生成,而${}则没有使用预编译,传入的参数直接和sql进行拼接,由此会产生sql注入的漏洞。
${}、#{}相同之处:
- 都可以 获取对象的值 (嵌套类型对象)
模糊查询
模糊查询,方式一:
like #{stuName}
student.setStuName(“%w%”);
<select id="queryStudentBystuageOrstuName" parameterType="student" resultType="student" >
select stuno,stuname,stuage from student where stuage= #{stuAge} or stuname like #{stuName}
</select>
List<Student> queryStudentBystuageOrstuName(Student student);
StudentMapper studentMapper = session.getMapper( StudentMapper.class) ;
Student student = new Student();
student.setStuAge(24);
student.setStuName("%w%");
List<Student> students = studentMapper.queryStudentBystuageOrstuName(student) ;//接口的方法->SQL
模糊查询,方式二:
like ‘%${stuName}%’
student.setStuName(“w”);
<select id="queryStudentBystuageOrstuName" parameterType="student" resultType="student" >
select stuno,stuname,stuage from student where stuage= #{stuAge} or stuname like '%${stuName}%'
</select>
List<Student> queryStudentBystuageOrstuName(Student student);
StudentMapper studentMapper = session.getMapper( StudentMapper.class) ;
Student student = new Student();
student.setStuAge(24);
student.setStuName("w");
List<Student> students = studentMapper.queryStudentBystuageOrstuName(student) ;//接口的方法->SQL
嵌套类型对象
Address.java
public class Address {
private String homeAddress;
private String schoolAddress;
public String getHomeAddress() {
return homeAddress;
}
public void setHomeAddress(String homeAddress) {
this.homeAddress = homeAddress;
}
public String getSchoolAddress() {
return schoolAddress;
}
public void setSchoolAddress(String schoolAddress) {
this.schoolAddress = schoolAddress;
}
}
Student.java包含Address的对象
private Address address;//家庭、学校
public Address getAddress() {
return address;
}
public void setAddress(Address address) {
this.address = address;
}
方式一
<select id="queryStudentByaddress" parameterType="address" resultType="student" > select stuno,stuname,stuage from student where homeaddress = #{homeAddress} or schooladdress = '${schoolAddress}' </select>List<Student> queryStudentByaddress(Address address);StudentMapper studentMapper = session.getMapper( StudentMapper.class) ; Address address = new Address(); address.setHomeAddress("xa"); address.setSchoolAddress("x"); List<Student> students = studentMapper.queryStudentByaddress(address) ;方式二:级联属性
<!-- 输入参数为 级联属性 --> <select id="queryStudentByaddress" parameterType="student" resultType="student" > select stuno,stuname,stuage from student where homeaddress = #{address.homeAddress} or schooladdress = '${address.schoolAddress}' </select>List<Student> queryStudentByaddress(Student address);StudentMapper studentMapper = session.getMapper( StudentMapper.class) ; Student student = new Student(); Address address = new Address(); address.setHomeAddress("xa"); address.setSchoolAddress("xxxxxx"); student.setAddress(address); List<Student> students = studentMapper.queryStudentByaddress(student) ;方式三:输入对象为HashMap:
<select id="queryStudentBystuageOrstuNameWithHashMap" parameterType="HashMap" resultType="student" > select stuno,stuname,stuage from student where stuage= #{stuAge} or stuname like '%${stuName}%' </select>List<Student> queryStudentBystuageOrstuNameWithHashMap(Map<String,Object> map);//String,ObjectStudentMapper studentMapper = session.getMapper( StudentMapper.class) ; Map<String,Object> studentMap = new HashMap<>(); studentMap.put("stuAge", 24) ; studentMap.put("stuName", "zs") ; List<Student> students = studentMapper.queryStudentBystuageOrstuNameWithHashMap (studentMap) ;//接口的方法->SQLwhere stuage= #{stuAge}
用map中key的值 匹配 占位符#{stuAge},如果匹配成功 就用map的value替换占位符
mybatis调用存储过程
创建存储过程
查询某个年级的 学生总数
输入:年级
输出:该年级的学生总数
create or replace procedure queryCountByGradeWithProcedure(gName in varchar, scount out number )
as
begin
select count(*) into scount from student where graname = gname ;
end;
/
根据学号删除学生
create or replace procedure deleteStuBynoWithProcedure(sno in number)
as
begin
delete from student where stuno = sno ;
end;
/
调用存储过程实现查询
<!-- 通过调用[存储过程] 实现查询 ,statementType="CALLABLE"
存储过程的输入参数,在mybatis用Map来传递(HashMap)
-->
<select id="queryCountByGradeWithProcedure" statementType="CALLABLE" parameterType="HashMap" >
{
CALL queryCountByGradeWithProcedure(
#{gName,jdbcType=VARCHAR,mode=IN},
#{scount,jdbcType=INTEGER,mode=OUT}
)
}
</select>
void queryCountByGradeWithProcedure(Map<String,Object> params );
StudentMapper studentMapper = session.getMapper( StudentMapper.class) ;
//通过map给 存储过程指定输入参数
Map<String,Object> params = new HashMap<>();
params.put("gName", "g1") ;//指定存储过程的输入参数gName的值是g1
studentMapper.queryCountByGradeWithProcedure(params);//调用存储过程,并传入输入参数
//获取存储过程的输出参数
Object count = params.get("scount") ;
其中 通过statementType=“CALLABLE”设置SQL的执行方式是存储过程。 存储过程的输入参数gName需要通过HashMap来指定 在使用时,通过hashmap的put方法传入输入参数的值;通过hashmap的Get方法 获取输出参数的值。
要注意Jar问题:ojdbc6.jar不能在 调存储过程时 打回车、tab,但是ojdbc7.jar可以。
如果报错: No enum constant org.apache.ibatis.type.JdbcType.xx,则说明mybatis不支持xx类型,需要查表。
调用存储过程实现删除
<!-- 通过存储过程实现删除 -->
<delete id="deleteStuBynoWithProcedure" statementType="CALLABLE" parameterType="HashMap">
{
CALL deleteStuBynoWithProcedure(
#{sno,jdbcType=INTEGER,mode=IN}
)
}
</delete>
void deleteStuBynoWithProcedure(Map<String,Object> params);
StudentMapper studentMapper = session.getMapper( StudentMapper.class) ;
Map<String,Object> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("sno", 3) ;
studentMapper.deleteStuBynoWithProcedure( map) ;
session.commit();
session.close();
存储过程 无论输入参数是什么值,语法上都需要 用map来传递该值;
只要 是 <transactionManager type="JDBC"/>,则增删改都需要手工commit ;
输出参数
输出参数resultType
简单类型(8个基本+String)
<select id="queryStudentCount" resultType="int" >
select count(*) from student
</select>
int queryStudentCount();
StudentMapper studentMapper = session.getMapper(StudentMapper.class) ;
int count = studentMapper.queryStudentCount();
输出参数为实体对象类型
<select id="queryStuByStuno" parameterType="int" resultType="student" >
select * from student where stuno = ${value}
</select>
Student queryStuByStuno(int stuno);
StudentMapper studentMapper = session.getMapper(StudentMapper.class) ;
Student student = studentMapper.queryStuByStuno(2) ;//接口中的方法->SQL语句
输出参数为实体对象类型的集合
虽然输出类型为集合,但是resultType依然写 集合的元素类型(resyltType=“Student”)
<select id="queryAllStudents" resultType="Student" >
select * from student
</select>
List<Student> queryAllStudents();
StudentMapper studentMapper = session.getMapper(StudentMapper.class);
List<Student> students = studentMapper.queryAllStudents();// 接口的方法->SQL
输出参数类型为HashMap
<!-- 别名作为Map的key -->
<select id="queryStudentOutByHashMap" resultType="HashMap" >
select stuno "no",stuname "name" from student where stuno=1
</select>
HashMap<String,Object> queryStudentOutByHashMap();
StudentMapper studentMapper = session.getMapper(StudentMapper.class) ;
HashMap<String,Object> studentMap = studentMapper.queryStudentOutByHashMap();
HashMap本身是一个集合,可以存放多个元素,但是根据提示发现 返回值为HashMap时 ,查询的结果只能是1个学生(no,name)
结论:一个HashMap 对应一个学生的多个元素(多个属性) 【一个map,一个学生】
比较像二维数组,一个数组是一个HashMap对象
{
{1,zs,23,xa}, 一个HashMap对象
{2,ls,24,bj},
{3,ww,25,tj}
}
获取多个HashMap
<select id="queryAllStudentsOutByHashMap" resultType="HashMap" >
select stuno "no",stuname "name" from student
</select>
List<HashMap<String,Object>> queryAllStudentsOutByHashMap();
StudentMapper studentMapper = session.getMapper(StudentMapper.class) ;
List<HashMap<String,Object>> studentMap = studentMapper.queryAllStudentsOutByHashMap();
resultType
resultMap:实体类的属性、数据表的字段: 类型、名字不同时(stuno,id)
注意:当属性名 和字段名 不一致时,除了使用resultMap以外,还可以使用resultType+HashMap:
resultMap
<select id="queryStudentById" parameterType="int" resultMap="queryStudentByIdMap" >
select id,name from student where id = #{id}
</select>
<resultMap type="student" id="queryStudentByIdMap">
<!-- 指定类中的属性 和 表中的字段 对应关系 -->
<id property="stuNo" column="id" />
<result property="stuName" column="name" />
</resultMap>
Student queryStudentById(int stuno);
StudentMapper studentMapper = session.getMapper(StudentMapper.class) ;
Student student = studentMapper.queryStudentById(2) ;//接口中的方法->SQL语句
resultType+HashMap
<select id="queryStudentByIdWithHashMap" parameterType="int" resultType="student" >
select id "stuNo",name "stuName" from student where id = #{id}
</select>
Student queryStudentByIdWithHashMap(int stuno);
StudentMapper studentMapper = session.getMapper(StudentMapper.class) ;
Student student = studentMapper.queryStudentByIdWithHashMap(2) ;//接口中的方法->SQL语句
select 表的字段名 “类的属性名” from… 来制定字段名 和属性名的对应关系
注意: 如果如果10个字段,但发现 某一个字段结果始终为默认值(0,0.0,null),则可能是 表的字段 和 类的属性名字写错。
动态SQL
//查询全部
String statement = "select stuno,stuname from student";
//根据年龄查询学生
String statement = "select stuno,stuname from student where stuage = #{stuage}";
//根据姓名和年龄查询学生
String statement = "select stuno,stuname from student where stuage = #{stuage} and stuage = #{stuage} ";
可以发现其中有重复的部分
<select id="queryStuByNOrAWishSQLTag" parameterType="student" resultType="student" >
select stuno,stuname,stuage from student
<where>
<!-- <if test="student有stuname属性 且不为null"> 属性严格区分大小写-->
<if test="stuName !=null and stuName!=''">
and stuname = #{stuName}
</if>
<if test="stuAge !=null and stuAge!=0 ">
and stuage = #{stuAge}
</if>
</where>
</select>
Student queryStuByNOrAWishSQLTag(Student student);
StudentMapper studentMapper = session.getMapper(StudentMapper.class) ;
Student stu = new Student();
stu.setStuAge(24);
//stu.setStuName("ls");
Student student = studentMapper.queryStuByNOrAWishSQLTag(stu) ;//接口中的方法->SQL语句
处理and的两种方式
方式一
<select id="queryStuByNOrAWishSQLTag" parameterType="student" resultType="student" > select stuno,stuname,stuage from student where 1=1 <if test="stuName !=null and stuName!='' "> and stuname = #{stuName} </if> <if test="stuAge !=null and stuAge!=0 "> and stuage = #{stuAge} </if> </select>方式二 (推荐)
<select id="queryStuByNOrAWishSQLTag" parameterType="student" resultType="student" > select stuno,stuname,stuage from student <where> <if test="stuName !=null and stuName!='' "> and stuname = #{stuName} </if> <if test="stuAge !=null and stuAge!=0 "> and stuage = #{stuAge} </if> </where> </select><where>会自动处理第一个(满足条件的第一个)<if>标签中的 and,但不会处理之后<if>中的and。
foreach
查询学号为1、2、53的学生信息
sql语句
select stuno,stuname from student where stuno in(1,2,53)
<foreach>迭代的类型:数组、对象数组、集合、属性(Grade类: List<Integer> ids)
属性
(Grade类: List<Integer> ids
public class Grade {
//学号
private List<Integer> stuNos ;
public List<Integer> getStuNos() {
return stuNos;
}
public void setStuNos(List<Integer> stuNos) {
this.stuNos = stuNos;
}
}
<!-- 将多个元素值 放入对象的属性中 -->
<select id="queryStudentsWithNosInGrade" parameterType="grade" resultType="student">
select * from student
<where>
<if test="stuNos!=null and stuNos.size>0">
<foreach collection="stuNos" open=" and stuno in (" close=")"
item="stuNo" separator=",">
#{stuNo}
</foreach>
</if>
</where>
</select>
collection:集合
select * from student
+open:
select * from student and stuno in (
+item:
select * from student and stuno in (1,2,53
+close:
select * from student and stuno in (1,2,53)
separator:分隔符
List<Student> queryStudentsWithNosInGrade(Grade grade);
StudentMapper studentMapper = session.getMapper( StudentMapper.class) ;
Grade grade = new Grade();
List<Integer> stuNos = new ArrayList<>();
stuNos.add(1) ;
stuNos.add(2) ;
// stuNos.add(53) ;
grade.setStuNos(stuNos);
List<Student> students = studentMapper.queryStudentsWithNosInGrade(grade) ;
简单类型的数组:
<!-- 将多个元素值 放入数组中 int[] stuNos = {1,2,53} -->
<select id="queryStudentsWithArray" parameterType="int[]" resultType="student">
select * from student
<where>
<if test="array!=null and array.length">
<foreach collection="array" open=" and stuno in (" close=")"
item="stuNo" separator=",">
#{stuNo}
</foreach>
</if>
</where>
</select>
约定:无论编写代码时,传递的是什么参数名(stuNos),在mapper.xml中 必须用array代替该数组
List<Student> queryStudentsWithArray(int[] stuNos);
StudentMapper studentMapper = session.getMapper( StudentMapper.class) ;
int[] stuNos = {1,2,53};
List<Student> students = studentMapper.queryStudentsWithArray(stuNos) ;
对象数组:
<sql id="objectArrayStunos">
<where>
<if test="array!=null and array.length>0">
<foreach collection="array" open=" and stuno in (" close=")"
item="student" separator=",">
#{student.stuNo}
</foreach>
</if>
</where>
</sql>
<!-- 将多个元素值 放入对象数组中Student[] students = {student0,student1,student2} 每个studentx包含一个学号属性 -->
<select id="queryStudentsWithObjectArray" parameterType="Object[]" resultType="student">
select * from student
<!--如果sql片段和 引用处不在同一个文件中,则需要 在refid 引用时 加上namespace: namespace.id
<include refid="org.lanqiao.mapper.abcMapper.objectArrayStunos"></include> -->
<include refid="objectArrayStunos"></include>
</select>
List<Student> queryStudentsWithObjectArray(Student[] students);
StudentMapper studentMapper = session.getMapper( StudentMapper.class) ;
Student stu1 = new Student();
stu1.setStuNo(1);
Student stu2 = new Student();
stu2.setStuNo(2);
Student stu53 = new Student();
stu53.setStuNo(53);
Student[] stus = new Student[] {stu1,stu2,stu53};
List<Student> students = studentMapper.queryStudentsWithObjectArray(stus);
集合:
无论编写代码时,传递的是什么参数名(stuNos),在mapper.xml中 必须用list代替该数组
<!-- 将多个元素值 放入数组中 List<Integer> stuNos 值 {1,2,53} -->
<select id="queryStudentsWithList" parameterType="list" resultType="student">
select * from student
<where>
<if test="list!=null and list.size>0">
<foreach collection="list" open=" and stuno in (" close=")"
item="stuNo" separator=",">
#{stuNo}
</foreach>
</if>
</where>
</select>
List<Student> queryStudentsWithList(List<Integer> stuNos);
List<Integer> stuNos = new ArrayList<>();
stuNos.add(1) ;
stuNos.add(2) ;
stuNos.add(53) ;
List<Student> students = studentMapper.queryStudentsWithList(stuNos) ;
SQL片段:
java:方法
数据库:存储过程、存储函数
Mybatis :SQL片段
- 提取相似代码
引用
<sql id="objectArrayStunos"> <where> <if test="array!=null and array.length>0"> <foreach collection="array" open=" and stuno in (" close=")" item="student" separator=","> #{student.stuNo} </foreach> </if> </where> </sql><select id="queryStudentsWithObjectArray" parameterType="Object[]" resultType="student"> select * from student <!--如果sql片段和 引用处不在同一个文件中,则需要 在refid 引用时 加上namespace: namespace.id <include refid="org.lanqiao.mapper.abcMapper.objectArrayStunos"></include> --> <include refid="objectArrayStunos"></include> </select>
关联查询
两张表
student
stuno
stuname
cardid
studentCard
cardid
cardinfo
一对一
业务扩展类
核心:用resultType指定类的属性 包含 多表查询的所有字段
resultMap
业务扩展类做法:
新建业务扩展类,类中既包含了A的属性也包含了B的属性,继承一个属性多的类,重写一个属性较少的类的属性
public class StudentBusiness extends Student{//学生业务扩展类
private int cardId;
private String cardInfo ;
public int getCardId() {
return cardId;
}
public void setCardId(int cardId) {
this.cardId = cardId;
}
public String getCardInfo() {
return cardInfo;
}
public void setCardInfo(String cardInfo) {
this.cardInfo = cardInfo;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return super.toString() + ","+this.cardId+","+this.cardInfo;
}
}
<select id="queryStudentByNoWithOO" parameterType="int"
resultType="StudentBusiness" >
select s.*,c.* from student s inner join studentcard c
on s.cardid=c.cardid
where s.stuno = #{stuNo}
</select>
StudentBusiness queryStudentByNoWithOO(int stuno);
StudentMapper studentMapper = session.getMapper(StudentMapper.class) ;
StudentBusiness studentBusiness = studentMapper.queryStudentByNoWithOO(2) ;//接口中的方法->SQL语句
resultMap的做法
表与表之间通过外键进行连接,那么,类与类之间通过属性进行连接
通过 属性成员 将2个类建立起联系
把其中一个类作为另一个的类的属性
//学生类 包含:1学生信息 2学生证信息
public class Student {
//1学生信息
private int stuNo ;
private String stuName ;
private int stuAge ;
private String graName ;
private boolean stuSex ;
//2学生证信息
private StudentCard card ;
/* x
x
x
x*/
}
<resultMap type="student" id="student_card_map">
<!-- 学生的信息 -->
<id property="stuNo" column="stuNo"/>
<result property="stuName" column="stuName" />
<result property="stuAge" column="stuAge" />
<!-- 一对一时,对象成员使用 association映射;javaType指定该属性的类型-->
<association property="card" javaType="StudentCard" >
<id property="cardId" column="cardId"/>
<result property="cardInfo" column="cardInfo"/>
</association>
</resultMap>
<!-- 利用resultMap实现一对一 -->
<select id="queryStudentByNoWithOO2" parameterType="int" resultMap="student_card_map" >
select s.*,c.* from student s inner join studentcard c
on s.cardid=c.cardid
where s.stuno = #{stuNo}
</select>
Student queryStudentByNoWithOO2(int stuNo);
StudentMapper studentMapper = session.getMapper(StudentMapper.class) ;
Student student = studentMapper.queryStudentByNoWithOO2(2) ;
一对多
(MyBatis:多对一,多对多的本质就是 一对多的变化)
表:
studentClass
classId
className
student
stuno
stuname
classId
其中两个学生对应一个班级
班级类中增加学生属性
public class StudentClass {
private int classId;
private String className;
//增加学生属性 (通过该字段 让Student类和StudentClass类建立起关联)
List<Student> students ;
/*x
x
x*/
}
<!-- 类-表的对应关系 -->
<resultMap type="studentClass" id="class_student_map">
<!-- 因为 type的主类是班级,因此先配置班级的信息-->
<id property="classId" column="classId"/>
<result property="className" column="className"/>
<!-- 配置成员属性学生,一对多;属性类型:javaType,属性的元素类型ofType -->
<collection property="students" ofType="student">
<id property="stuNo" column="stuNo"/>
<result property="stuName" column="stuName"/>
<result property="stuAge" column="stuAge"/>
</collection>
</resultMap>
可以级联匹配,student中在配置studentcard的信息
查询g1班的班级信息,和g1班的所有学生信息
<select id="queryClassAndStudents" parameterType="int" resultMap="class_student_map">
select c.*,s.* from student s
inner join studentclass c
on c.classid = s.classid
where c.classid = #{classId}
</select>
StudentClass queryClassAndStudents(int classId);
StudentClassMapper studentClassMapper = session.getMapper(StudentClassMapper.class) ;
//班级
List<StudentClass> studentClasses = studentClassMapper.queryClassAndStudents() ;
//班级信息
for(StudentClass stuClass :studentClasses) {
System.out.println(stuClass.getClassId()+","+stuClass.getClassName());
System.out.println("-----------");
for(Student student: stuClass.getStudents()) {
System.out.println(student.getStuNo()+","+student.getStuName());
}
}
日志
如果不指定,Mybatis就会根据以下顺序 寻找日志
SLF4J →Apache Commons Logging →Log4j2 → Log4j →JDK logging
使用log4j
jar
Log4j: log4j.jar (mybatis.zip中lib中包含此jar)
开启日志,conf.xml
<settings>
<!-- 开启日志,并指定使用的具体日志 -->
<setting name="logImpl" value="LOG4J"/>
</settings>
编写配置日志输出文件 log4j.properties
log4j.properties,内容
log4j.rootLogger=DEBUG, stdout
log4j.appender.stdout=org.apache.log4j.ConsoleAppender
log4j.appender.stdout.layout=org.apache.log4j.PatternLayout
log4j.appender.stdout.layout.ConversionPattern=%5p [%t] - %m%n
DEBUG:级别
日志级别:
DEBUG<INFO<WARN<ERROR
如果设置为info,则只显示 info及以上级别的信息;
建议:在开发时设置debug,在运行时设置为info或以上。
stdout:在控制台输出
可以通过日志信息,相信的阅读mybatis执行情况( 观察mybatis实际执行sql语句 以及SQL中的参数 和返回结果)
延迟加载(懒加载):
一对一、一对多、多对一、多对多
一对多:班级-学生 ,
如果不采用延迟加载 (立即加载),查询时会将 一 和多 都查询,班级、班级中的所有学生。
如果想要 暂时只查询1的一方, 而多的一方 先不查询 而是在需要的时候再去查询 –>延迟加载
mybatis中使用延迟加载,需要先配置:
<settings>
<!-- 开启延迟加载 -->
<setting name="lazyLoadingEnabled" value="true"/>
<!-- 关闭立即加载 -->
<setting name="aggressiveLazyLoading" value="false"/>
</settings>
一对一:学生(student)、学生证(studentCard)
studentCardMapper.xml
<mapper namespace="org.lanqiao.mapper.StudentCardMapper">
<!-- 查询学生证信息 -->
<select id="queryCardById" parameterType="int" resultType="studentCard">
<!-- 查询学生对应的学生证 -->
select * from studentCard where cardid = #{cardId}
</select>
<!-- 根据cardid查询学生证的SQL: org.lanqiao.mapper.StudentCardMapper.queryCardById -->
</mapper>
加载mapper配置文件
<mapper resource="org/lanqiao/mapper/studentCardMapper.xml"/>
<resultMap type="student" id="student_card_lazyLoad_map">
<!-- 学生的信息 -->
<id property="stuNo" column="stuNo"/>
<result property="stuName" column="stuName" />
<result property="stuAge" column="stuAge" />
<!-- 一对一时,对象成员使用 association映射;javaType指定该属性的类型
此次采用延迟加载:在查询学生时,并不立即加载 学生证信息
-->
<!-- 学生证 ,通过select 在需要的时候再查学生证 -->
<association property="card" javaType="StudentCard" select="org.lanqiao.mapper.StudentCardMapper.queryCardById" column="cardid" >
</association>
</resultMap>
<!-- 利用resultMap实现一对一 ,延迟加载-->
<select id="queryStudentWithOO2LazyLoad" parameterType="int" resultMap="student_card_lazyLoad_map" >
<!-- 先查学生 -->
select * from student
</select>
List<Student> queryStudentWithOO2LazyLoad();
StudentMapper studentMapper = session.getMapper(StudentMapper.class) ;
//学生,
List<Student> students = studentMapper.queryStudentWithOO2LazyLoad();
//此时,只获取了学生的信息
for(Student student:students) {
System.out.println(student.getStuNo()+","+student.getStuName());
//获取学生证,下一步即将获取学生证的信息
StudentCard card = student.getCard() ;
System.out.println(card.getCardId()+","+card.getCardInfo());
}
session.close();
如果增加了mapper.xml ,要修改conf.xml配置文件(将新增的mapper.xml加载进去)
通过debug可以发现, 如果程序只需要学生,则只向数据库发送了查询学生的SQL;当我们后续 需要用到学生证的时候,再第二次发送 查询学生证的SQL。
一对多:和一对一的延迟加载配置方法相同
延迟加载的步骤:先查班级,按需查询学生
开启延迟加载conf.xml配置settings
配置mapper.xml
StudentClassMapper.xml
<!-- 一对多,带延迟加载 -->
<select id="queryClassAndStudents" resultMap="class_student_lazyLoad_map">
<!-- 先查询班级 -->
select c.* from studentclass c
</select>
<!-- 类-表的对应关系 -->
<resultMap type="studentClass" id="class_student_lazyLoad_map">
<id property="classId" column="classId"/>
<result property="className" column="className"/>
<!-- 再查班级对应的学生 -->
<collection property="students" ofType="student" select="org.lanqiao.mapper.StudentMapper.queryStudentsByClassId" column="classid">
</collection>
</resultMap>
StudentMapper.xml
<!-- 一对多,延迟加载需要的: 查询班级中的所有学生 -->
<select id="queryStudentsByClassId" parameterType="int" resultType="student">
select * from student where classId = #{classId}
</select>
StudentClassMapper.java
//查询全部班级
List<StudentClass> queryClassAndStudents();
StudentClassMapper studentClassMapper = session.getMapper(StudentClassMapper.class) ;
//班级
List<StudentClass> studentClasses = studentClassMapper.queryClassAndStudents() ;
//班级信息
for(StudentClass stuClass :studentClasses) {
System.out.println(stuClass.getClassId()+","+stuClass.getClassName());
System.out.println("-----------");
for(Student student: stuClass.getStudents()) {
System.out.println(student.getStuNo()+","+student.getStuName());
}
}
session.close();
即查询 学生的sql是通过 select属性指定,并且通过column指定外键
查询缓存
只涉及查询
一级缓存 :同一个SqlSession对象
MyBatis默认开启一级缓存,如果用同样的SqlSession对象查询相同的数据,则只会在第一次 查询时 向数据库发送SQL语句,并将查询的结果 放入到SQLSESSION中(作为缓存在);后续再次查询该同样的对象时,则直接从缓存中查询该对象即可(即省略了数据库的访问)
执行commit操作后会将缓存清空
二级缓存
MyBatis默认情况没有开启二级缓存,需要手工打开。
conf.xml
<!-- 开启二级缓存 --> <setting name="cacheEnabled" value="true"/>在具体的mapper.xml中声明开启
<!-- 声明次namespace开启二级缓存 --> <cache/>
根据异常提示:NotSerializableException可知,MyBatis的二级缓存 是将对象放入硬盘文件中(序列化)
序列化:内存->硬盘
反序列化:硬盘->内存
准备缓存的对象,必须实现了序列化接口 (如果开启的缓存Namespace=“org.lanqiao.mapper.StudentMapper”),可知序列化对象为Student,因此需要将Student序列化 (序列化Student类,以及Student的级联属性、和父类)
public class Student implements Serializable{}
public class StudentCard implements Serializable{}
二级缓存,实际存放的位置在硬盘中
触发将对象写入二级缓存的时机:SqlSession对象的close()方法。将一级缓存的对象放入硬盘
日志中会发现有Cache Hit Ratio[xxxx]:0.0和Cache Hit Ratio[xxxx]:0.5,它的意思是命中率的问题。
第一次查询时,二级缓存中没有,因此是0.0;第二次之前已经close了,因此将查询结果放入二级缓存;第二次查询,总共查询了两次,查到了结果,因此命中率是0.5
命中率:
1:zs :0%
2: 50%
3: 2/3 0.666
4: 3/4 0.75
Mybatis自带二级缓存:【同一个namespace】生成的mapper对象
回顾:namespace的值 就是 接口的全类名(包名.类名), 通过接口可以产生代理对象(studentMapper对象—>namespace决定了studentMapper对象的产生
结论:只要产生的xxxMapper对象 来自于同一个namespace,则 这些对象 共享二级缓存。
如果是同一个SqlSession对象进行多次相同的查询,则直接进入一级缓存查询;如果不是同一个SqlSession对象进行多次相同的查询(但是来自于同一个namespace)则进入二级缓存查询
注意:二级缓存 的范围是同一个namespace, 如果有多个xxMapper.xml的namespace值相同,则通过这些xxxMapper.xml产生的xxMapper对象 仍然共享二级缓存。
禁用 :select标签中添加属性
useCache="false"
清理:
与清理一级缓存的方法相同commit();
commit(); (一般执行增删改时 会清理掉缓存;设计的原因 是为了防止脏数据)
在二级缓存中,commit()不能是查询自身的commit。(session.commit;)
commit会清理一级和二级缓存;但是 清理二级缓存时,不能是查询自身的commit;
在select标签中 增加属性
flushCache="true"
MyBatis中调用SqlSession.commit()和SqlSession.close()对二级缓存的影响
三方提供的二级缓存:
ehcache、memcache
要想整合三方提供的二级缓存 (或者自定义二级缓存),必须实现org.apache.ibatis.cache.Cache接口,该接口的默认实现类是PerpetualCache
整合ehcache二级缓存:
jar
ehcache-core.jar mybatis-Ehcache.jar slf4j-api.jar编写ehcache配置文件 Ehcache.xml
<ehcache xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:noNamespaceSchemaLocation="../config/ehcache.xsd"> <diskStore path="D:\Ehcache"/> <defaultCache maxElementsInMemory="1000" maxElementsOnDisk="1000000" eternal="false" overflowToDisk="false" timeToIdleSeconds="100" timeToLiveSeconds="100" diskExpiryThreadIntervalSeconds="120" memoryStoreEvictionPolicy="LRU"> </defaultCache> </ehcache>当二级缓存的对象 超过内存限制时(缓存对象的个数>maxElementsInMemory),存放入的硬盘文件
<diskStore path="D:\Ehcache"/>maxElementsInMemory:设置 在内存中缓存 对象的个数 maxElementsOnDisk:设置 在硬盘中缓存 对象的个数 eternal:设置缓存是否 永远不过期 overflowToDisk:当内存中缓存的对象个数 超过maxElementsInMemory的时候,是否转移到硬盘中 timeToIdleSeconds:当2次访问 超过该值的时候,将缓存对象失效 timeToLiveSeconds:一个缓存对象 最多存放的时间(生命周期) diskExpiryThreadIntervalSeconds:设置每隔多长时间,通过一个线程来清理硬盘中的缓存 memoryStoreEvictionPolicy:当超过缓存对象的最大值时,处理的策略;LRU,FIFO,LFU开启EhCache二级缓存
在xxxMapper.xml中开启
<cache type="org.mybatis.caches.ehcache.EhcacheCache"> <!-- 通过property覆盖Ehcache.xml中的值 --> <property name="maxElementsInMemory" value="2000"/> <property name="maxElementsOnDisk" value="3000"/> </cache>
逆向工程
表、类、接口、mapper.xml四者密切相关,因此 当知道一个的时候 其他三个应该可以自动生成。
表->其他三个
实现步骤:
jar
mybatis-generator-core.jar mybatis.jar ojdbc.jar逆向工程的配置文件generator.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <!DOCTYPE generatorConfiguration PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD MyBatis Generator Configuration 1.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-generator-config_1_0.dtd"> <generatorConfiguration> <context id="DB2Tables" targetRuntime="MyBatis3"> <commentGenerator> <!-- suppressAllComments属性值:是否不出现注释 true:自动生成实体类、SQL映射文件时没有注释 false:自动生成实体类、SQL映射文件,并附有注释 --> <property name="suppressAllComments" value="true" /> </commentGenerator> <!-- 数据库连接信息 --> <jdbcConnection driverClass="oracle.jdbc.OracleDriver" connectionURL="jdbc:oracle:thin:@127.0.0.1:1521:ORCL" userId="scott" password="tiger"> </jdbcConnection> <!-- forceBigDecimals属性值: true:把数据表中的DECIMAL和NUMERIC类型, 解析为JAVA代码中的java.math.BigDecimal类型 false(默认):把数据表中的DECIMAL和NUMERIC类型, 解析为解析为JAVA代码中的Integer类型 --> <javaTypeResolver> <property name="forceBigDecimals" value="false" /> </javaTypeResolver> <!-- targetProject属性值:实体类的生成位置 targetPackage属性值:实体类所在包的路径 --> <javaModelGenerator targetPackage="org.lanqiao.entity" targetProject=".\src"> <!-- trimStrings属性值: true:对数据库的查询结果进行trim(去空格)操作 false(默认):不进行trim操作 --> <property name="trimStrings" value="true" /> </javaModelGenerator> <!-- targetProject属性值:SQL映射文件的生成位置 targetPackage属性值:SQL映射文件所在包的路径 --> <sqlMapGenerator targetPackage="org.lanqiao.mapper" targetProject=".\src"> </sqlMapGenerator> <!-- 生成动态代理的接口 --> <javaClientGenerator type="XMLMAPPER" targetPackage="org.lanqiao.mapper" targetProject=".\src"> </javaClientGenerator> <!-- 指定数据库表 --> <table tableName="Student"> </table> <table tableName="studentCard"> </table> <table tableName="studentClass"> </table> </context> </generatorConfiguration>执行
public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, XMLParserException, InvalidConfigurationException, SQLException, InterruptedException { File file = new File("src/generator.xml") ;//配置文件 List<String> warnings = new ArrayList<>(); ConfigurationParser cp = new ConfigurationParser(warnings); Configuration config = cp.parseConfiguration(file); DefaultShellCallback callBack = new DefaultShellCallback(true); //逆向工程的核心类 MyBatisGenerator generator = new MyBatisGenerator(config, callBack,warnings ); generator.generate(null); } }
数据库环境切换 (驱动jar)
切换 environment (指定实际使用的数据库)
<!--default指定環境 --> <environments default="devOracle"> <!--oracle --> <environment id="devOracle"> <transactionManager type="JDBC" /> <!-- 配置数据库连接信息 --> <dataSource type="POOLED"> <property name="driver" value="${oracle.driver}" /> <property name="url" value="${oracle.url}" /> <property name="username" value="${oracle.username}" /> <property name="password" value="${oracle.password}" /> </dataSource> </environment> <!--mysql --> <environment id="devMysql"> <transactionManager type="JDBC" /> <!-- 配置数据库连接信息 --> <dataSource type="POOLED"> <property name="driver" value="${mysql.driver}" /> <property name="url" value="${mysql.url}" /> <property name="username" value="${mysql.username}" /> <property name="password" value="${mysql.password}" /> </dataSource> </environment> </environments>db.properties
#oracle oracle.driver=oracle.jdbc.OracleDriver oracle.url=jdbc:oracle:thin:@127.0.0.1:1521:ORCL oracle.username=scott oracle.password=tiger #mysql mysql.driver=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver mysql.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mydb?allowMultiQueries=true mysql.username=root mysql.password=root配置 Provider别名
<!-- 配置数据库支持类,value的值是别名--> <databaseIdProvider type="DB_VENDOR"> <property name="MySQL" value="mysql" /> <property name="Oracle" value="oracle" /> </databaseIdProvider>写不同数据库的SQL语句
在mappe.xml中配置databaseId=“Provider别名”、
<!--mysql--> <select id="queryStudentByNo" resultType="com.yanqun.entity.Student" parameterType="int" databaseId="mysql"> select * from student where stuNo=#{stuNo} </select><!-- oracle--> <select id="queryStudentByNo" parameterType="student" resultType="student" databaseId="oracle"> select * from student where stuNo=#{stuNo} </select>id值相同,系统会根据环境的不同选择执行的语句
如果mapper.xml的 sql标签 仅有 一个 不带databaseId的标签,则改标签 会自动适应当前数据库。如果既有不带databaseId的标签,又有带databaseId的标签,则程序会优先使用带databaseId的标签
注解方式
推荐使用xml
将sql语句写在接口的方法上@Select(“”) ;xxMapper.java
//
@Select("select * from student where stuNo = #{stuNo}")
Student queryStudentByNo (int stuNo);
将接口的全类名 写入,让mybatis知道sql语句此时是存储在接口中conf.xml
<mappers>
<mapper class="com.yanqun.mapper.StudentMapper" />
</mappers>
注解/xml都支持批量引入,
<mappers>
<!--以下可以将com.yanqun.mapper 包中的注解接口 和 xml全部一次性引入 -->
<package name="com.yanqun.mapper" />
</mappers>
增删改的返回值问题
返回值可以是void、Integer、Long、Boolean 如何操作:只需要在接口中 修改返回值即可,映射文件不需要任何其他的操作
事务自动提交
手动提交:
sessionFactory.openSession();
session.commit();//提交
自动提交:每个dml语句 自动提交
sessionFactory.openSession(true);
自增问题
mysql支持自增
表
create table student
(
stuno int(4) primary key auto_increment,
stuname varchar(10),
stuage int(4),
graname varchar(10)
);
自增的同时将值回写
<insert id="addStudent"
parameterType="com.lx.entity.Student" databaseId="mysql" useGeneratedKeys="true" keyProperty="stuNo">
insert into student(stuName,stuAge,graName)
values(#{stuName},#{stuAge},#{graName})
</insert>
只需要配置两个属性即可:
useGeneratedKeys="true" keyProperty="stuNo"
获取自增值
student.getStuNo();
oracle不支持自增 :通过序列模拟实现
创建序列
create sequence myseq
increment by 1
start with 1;
序列自带的两个属性:
nextval:序列中下一个值
currval: 当前值
插入值
insert into student values(myseq.nextval,'zs1',23,'a1');
insert into student values(myseq.nextval,'zs2',24,'a2');
insert into student values(myseq.nextval,'zs3',25,'a3');
insert into student values(myseq.nextval,'zs4',26,'a4');
insert into student values(myseq.nextval,'zs5',27,'a5');
方式一:before(推荐)
通过 <insert>的子标签 <selectKey>实现:
在 <selectKey>中查询下一个序列(自增后的值),再将此值传入keyProperty=“stuNo”属性,最后在真正执行时 使用该属性值。
<insert id="addStudent"
parameterType="com.yanqun.entity.Student" databaseId="oracle">
<!--order="BEFORE"表示先执行selectKey标签,将myseq.nextval的值拿到,放入keyProperty="stuNo"中-->
<selectKey keyProperty="stuNo" resultType="Integer" order="BEFORE">
select myseq.nextval from dual
</selectKey>
insert into student(stuno,stuName,stuAge,graName)
values(#{stuNo} , #{stuName},#{stuAge},#{graName})
</insert>
方式二:after
<insert id="addStudent"
parameterType="com.yanqun.entity.Student" databaseId="oracle">
<selectKey keyProperty="stuNo" resultType="Integer" order="AFTER">
select myseq.currval from dual
</selectKey>
insert into student(stuno,stuName,stuAge,graName)
values(myseq.nextval , #{stuName},#{stuAge},#{graName})
</insert>
先执行sql语句,将数据插入在执行selectKey标签,将值回写,插入时使用的myseq.nextval,因此回写时使用的是myseq.currval
参数问题
目前 将多个参数封装到一个javabean对象(pojo),然后使用该对象传递
传入多个参数时,不用在mapper.xml中编写parameterType(输入参数不用写)
异常提示:
stuNo不能使用。可以使用的是:
[arg3, arg2, arg1, arg0, param3, param4, param1, param2]
<insert id="addStudent" databaseId="oracle">
insert into student(stuno,stuName,stuAge,graName)
values(#{arg0} , #{arg1},#{arg2},#{arg3})
</insert>
或
values(#{param1},#{param2},#{param3},#{param4})
注意param1从1开始计数arg0从0开始计数
public abstract Integer addStudent(Integer stuNo, String stuName, Integer stuAge,String graName);
StudentMapper studentMapper = session.getMapper(StudentMapper.class);//接口
Student stu = new Student(555, "bbb", 44, "xx");
studentMapper.addStudent( stu);
命名参数
可以在接口中通过@Param(“sNo”) 指定sql中参数的名字
<insert id="addStudent" databaseId="oracle">
insert into student(stuno,stuName,stuAge,graName)
values(#{sNo} , #{sName},#{sAge},#{gName})
</insert>
public abstract Integer addStudent(@Param("sNo") Integer stuNo, @Param("sName")String stuName, @Param("sAge")Integer stuAge, @Param("gName")String graName);
StudentMapper studentMapper = session.getMapper(StudentMapper.class);//接口
Student stu = new Student(555, "aaa", 44, "xx");
studentMapper.addStudent( stu);
综合使用
<insert id="addStudent" databaseId="oracle">
insert into student(stuno,stuName,stuAge,graName)
values(#{sNo} , #{stu.stuName},#{stu.stuAge},#{stu.graName})
</insert>
Integer addStudent(@Param("sNo")Integer stuNo, @Param("stu")Student student);
StudentMapper studentMapper = session.getMapper(StudentMapper.class);//接口
Student stu = new Student(null, "xx", 44, "xx");
studentMapper.addStudent(444,stu);
增加null
Student stu = new Student(555, null, 44, "xx");
studentMapper.addStudent( stu);
oracle: 如果插入的字段是Null, 提示错误: Other 而不是null
mysql:如果插入的字段是Null, 可以正常执行(没有约束)
原因:
各个数据库 在mybatis中 对各种数据类型的 默认值不一致。
mybatis中,jdbcTypeForNull(如果是null) ,则默认值OTHER。对于Other来说,MySQL能够处理(NULL),但是Oracle不行。
解决:
oracle: null ->OTHER ,需要手工告诉oracle :other ->null
方法一:修改具体的sql标签
当某个数据类型oracle无法处理时,告诉它用默认值null;
注意,此时设置的jdbcType=NULL,不会影响正常的赋值(“zs”)
<insert id="addStudent" databaseId="oracle">
insert into student(stuno,stuName)
values(#{stuNo} , #{stuName,jdbcType=NULL})
</insert>
jdbcType=NULL表示,当且仅当oracle遇到不能处理的值的时候,赋值为null
方法二:配置 mybatis全局配置文件conf.xml
<settings>
<setting name="jdbcTypeForNull" value="NULL"/>
</settings>
null ->jdbcTypeForNull -> NULL
返回值为HashMap的情况
<select id="queryStudentOutByHashMap" parameterType="int"
resultType="HashMap">
select stuNo "no",stuName "name",stuAge "age"
from student where stuNo = #{stuNo}
</select>
HashMap<String,Object> queryStudentOutByHashMap(int stuNo);
StudentMapper studentMapper = session.getMapper(StudentMapper.class);
HashMap<String, Object> studentMap
= studentMapper.queryStudentOutByHashMap(11);
//System.out.println( studentMap.get("no") +"," +studentMap.get("name") +"," +studentMap.get("age") );
System.out.println(studentMap);
select stuNo "no" ...其中 stuNo是数据库的字段名。
“no”是stuNo的别名,用于 在map中 get值时使用(作为map的key)。 map.get("no" );
如果不加别名,则map的key就是字段名
<select id="queryStudentOutByHashMap" parameterType="int"
resultType="HashMap">
select stuNo,stuName,stuAge
from student where stuNo = #{stuNo}
</select>
查询结果为HashMap的集合
<select id="queryStudentsByHashMap"
resultType="HashMap">
select stuNo ,stuName ,stuAge from student
</select>
@MapKey("STUNO")
HashMap<String,Student> queryStudentsByHashMap();
程序根据select的返回值 知道map的value就是 Student ,根据 @MapKey("stuNo")知道 Map的key是stuNo
@MapKey("STUNO") //oracle的元数据(字段名、表名 )都是大写
StudentMxapper studentMapper = session.getMapper(StudentMapper.class);
HashMap<String, Student> studentMap= studentMapper.queryStudentsByHashMap();
System.out.println( studentMap.get("no") +"," +studentMap.get("name") +"," +studentMap.get("age") );
session.close();
map:
key:STUNO value:Student
ResultMap : 字段 和 属性名 的对应关系
字段名 — 属性名 不一致
sno - stuNo
<!-- 如果字段名 属性名不一致,需要使用resultMap指定对应关系-->
<select id="queryStudentsWithResultMap" parameterType="int" resultMap ="studentResultMap">
select sno, sname, sage, gname from student
where sno = #{sno}
</select>
<resultMap type="com.yanqun.entity.Student" id="studentResultMap">
<!--主键 -->
<id column="sno" property="stuNo"/>
<!--普通字段
<result column="sname" property="stuName"/> -->
<result column="sage" property="stuAge"/>
<result column="gname" property="graName"/>
</resultMap>
鉴别器
<!-- 如果字段名 属性名不一致,需要使用resultMap指定对应关系-->
<select id="queryStudentsWithResultMap"
resultMap ="studentResultMap">
select sno, sname,nickname, sage, gname from student
</select>
<resultMap type="com.yanqun.entity.Student" id="studentResultMap">
<!--主键 -->
<id column="sno" property="stuNo"/>
<!--普通字段
<result column="sname" property="stuName"/> -->
<result column="sage" property="stuAge"/>
<result column="gname" property="graName"/>
<!-- 鉴别器 : 对查询结果进行分支处理: 如果是a年级,则真名,如果b年级,显示昵称-->
<discriminator javaType="string" column="gname">
<case value="a" resultType="com.yanqun.entity.Student" >
<result column="sname" property="stuName"/>
</case>
<case value="b" resultType="student">
<result column="nickname" property="stuName"/>
</case>
</discriminator>
</resultMap>
List<Student> queryStudentsWithResultMap();
StudentMapper studentMapper = session.getMapper(StudentMapper.class);//接口
List<Student> students= studentMapper.queryStudentsWithResultMap();
在resultMap中 还可以使用鉴别器:对相同sql中不同字段值进行判断,从而进行不同的处理。
别名问题
conf.xml
<typeAliases>
<!-- 给com.yanqun.entity包(包和子包)中的所有类 起了别名: 不带包名的类名,不区分大小写-->
<package name="com.yanqun.entity" ></package>
</typeAliases>
如果在批量设置别名时,出现了冲突。可以使用@Alias(“myStudent”)区分。
@Alias("myStudent")
public class Student {}
SQL标签
ONGL技术
<select id="queryStudentByNoWithONGL" parameterType="student" resultType="student"
databaseId="oracle">
<!-- select * from student where 1=1 -->
select * from student
<trim prefix="where" suffixOverrides="and">
<bind name="_queryName" value="'%'+stuName+'%'"/>
<if test="stuName != null and stuName !='' ">
stuName like #{stuName} and
</if>
<if test="graName != null and graName !='' ">
graName like '%${graName}%' and
</if>
<if test="stuAge != null and stuAge !='' ">
stuAge = #{stuAge} and
</if>
</trim>
<!--
<trim prefix="where" prefixOverrides="and">
<if test="stuName != null and stuName !='' ">
and stuName like '%${stuName}%'
</if>
<if test="graName != null and graName !='' ">
and graName like '%${graName}%'
</if>
<if test="stuAge != null and stuAge !='' ">
and stuAge = #{stuAge}
</if>
</trim>
-->
<!--
<where>
<if test="stuName != null and stuName !='' ">
and stuName like '%${stuName}%'
</if>
<if test="graName != null and graName !='' ">
and graName like '%${graName}%'
</if>
<if test="stuAge != null and stuAge !='' ">
and stuAge = #{stuAge}
</if>
</where>
-->
</select>
<where>可以处理拼接sql中 【开头】第一个and
<trim>可以处理拼接sql中 【开头或结尾】第一个and
开头:
<trim prefix="where" prefixOverrides="and">
给拼接的SQL加prefix="where"
prefixOverrides="and",处理拼接SQL中【开头】第一个and
suffixOverrides="and",处理拼接SQL中【结尾】最后一个and
prefix: 拼接
prefixOverrides:删除
内置参数
_parameter: 代表mybatis的输入参数。
_databaseId: 代表当前数据库的 名字
_parameter
<if test="_parameter.stuName != null and _parameter.stuName !='' ">
stuName like '%${_parameter.stuName}%' and
</if>
_databaseId
<if test="_databaseId == 'oracle'">
select * from student where stuNo = #{_parameter}
</if>
<if test="_databaseId == 'mysql'">
select * from student where stuNo != #{_parameter}
</if>
模糊查询三种方法
${} :原样输出
#[]:加引号
方法一${}
stuName like '%${stuName}%'
方法二:传值时,直接传 #{}
stuName like #{stuName}
student.setStuName("%s%");
方法三:bind参数
<bind name="_queryName" value="'%'+stuName+'%'"/>
stuName like #{_queryName}
通过bind将传入的stuName进行了处理(增加了%…%)
逆向工程的使用
生成逆向工程的文件
增加 mybatis配置文件 conf.xml
查询所有学生
//Example中的Criteria:查询条件
List<Student> students = mapper.selectByExample(null) ;
public class TestGeneratorDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
String resource = "conf.xml";
Reader reader = Resources.getResourceAsReader(resource);
SqlSessionFactory sessionFactory
= new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(reader);
SqlSession session = sessionFactory.openSession();
StudentMapper mapper = session.getMapper(StudentMapper.class);
//Example中的Criteria:查询条件
// List<Student> students = mapper.selectByExample(null) ;
//规则:example 默认使用的是 第一个criteria
StudentExample example = new StudentExample() ;
StudentExample.Criteria criteria = example.createCriteria();
// criteria.andStunoBetween((short) 32, (short) 33);// stuno: 2-3
criteria.andStunameLike("%l%");
//where (xx=xx and xx =x) or (xx =xxx and xx =xx) ;
//where stuname like '%z%' or ( stuno <=31 and granameLike "%j%) ;
//criteria:where stuname like '%z%'
// or
//criteria: stuno <=31 and granameLike "%j% ;
StudentExample.Criteria criteria1 = example.createCriteria();
criteria1.andStunoLessThanOrEqualTo((short)31) ; //<=
criteria1.andGranameLike("%j%") ;
example.or(criteria1) ;
//query by Criteria , QBC
List<Student> students = mapper.selectByExample(example ) ;
System.out.println(students );
session.close();
}
}
对于like模糊查询,逆向工程需要在传值时 写入%x%
MyBatis架构和源码解析
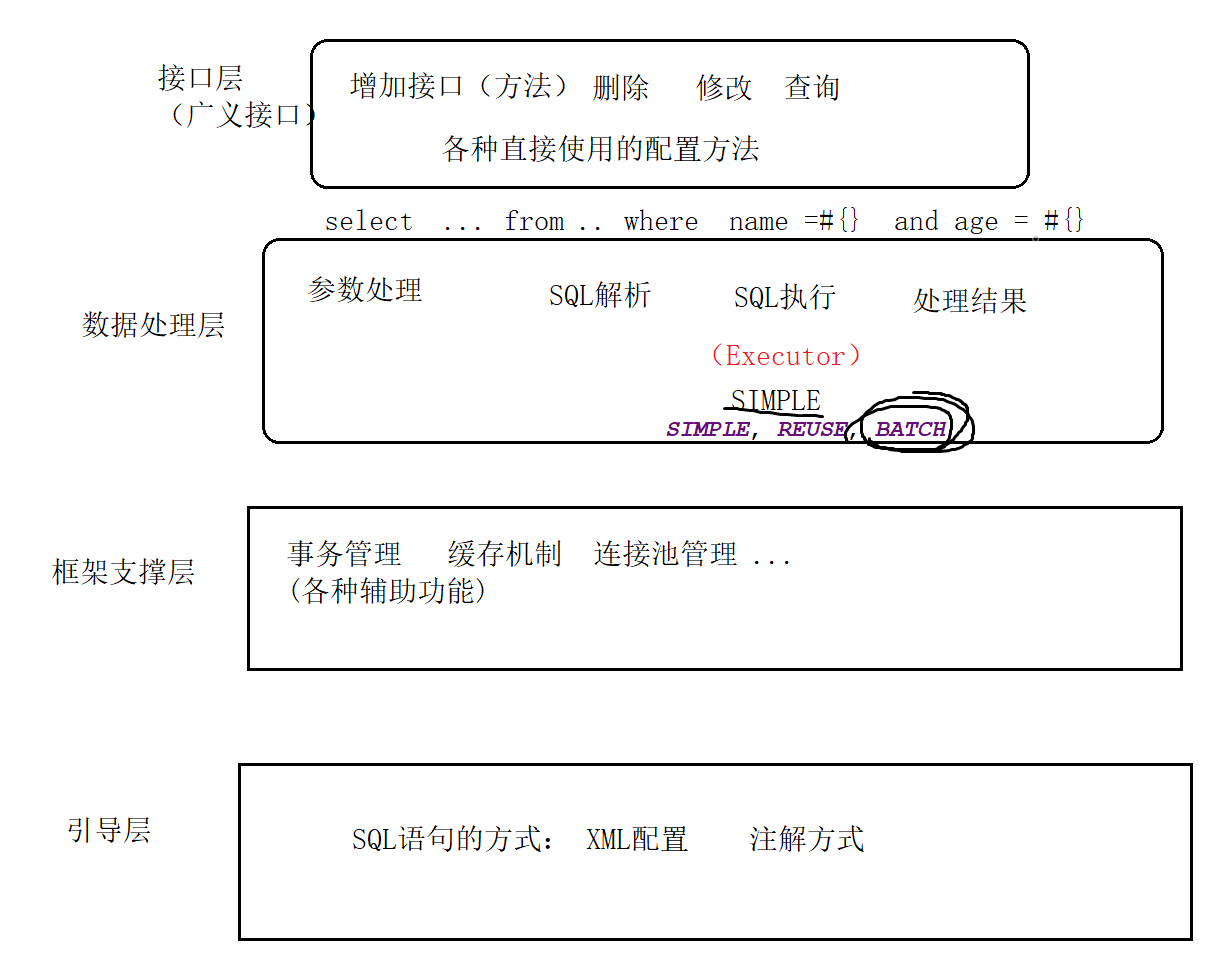 MyBatis中步骤
MyBatis中步骤
a.获取SqlSessionFactory对象
b.获取SqlSession对象
c.获取XxxMapper对象(代理接口中的方法、mapper.xml中的<select>等标签)
d.执行<select>等标签中定义的SQL语句
获取SqlSessionFactory对象
parser解析器
通过parseConfiguration()在configuration标签 设置了 properties、settings、 environments等属性标签
将所有的配置信息 放在了Configuration对象中
解析所有的XxxMapper.xml文件(分析其中的 增删改查标签)
<select id="" resultType=" 等属性 是通过 parseStatementNode()解析的
会将XxxMapper.xml中的<select>等标签解析成 MappedStatement对象即 MappedStatement对象就是 <select>等标签
MappedStatement ->存在于Configuration中
environment ->存在于Configuration中
所有的配置信息、增删改标签 全部存在于Configuration中
Configuration又存在于DefaultSqlSessionFactory对象中(SqlSessionFactory)
SqlSessionFactory对象 ->DefaultSqlSessionFactory ->Configuration ->包含了一切配置信息
获取SqlSession对象
configuration.newExecutor(tx, execType) ->SimpleExecutor(默认)
根据不同的类型execType,产生不同的Executor,并且会对执行器进行拦截操作:
executor = (Executor) interceptorChain.pluginAll(executor);
通过装饰模式,将刚才产生的executor 包装成一个更加强大的 executor。
作用:以后 如果我们要给MyBatis写自己的插件, 就可以通过拦截器实现。
插件开发:
1. 写插件
2. 放入拦截器
返回DefaultSqlSession(configuration,executor,事务)
SqlSession -》openSession()->openSessionFromDataSource()->DefaultSqlSession对象
SqlSession -》 DefaultSqlSession对象 -》执行SQL
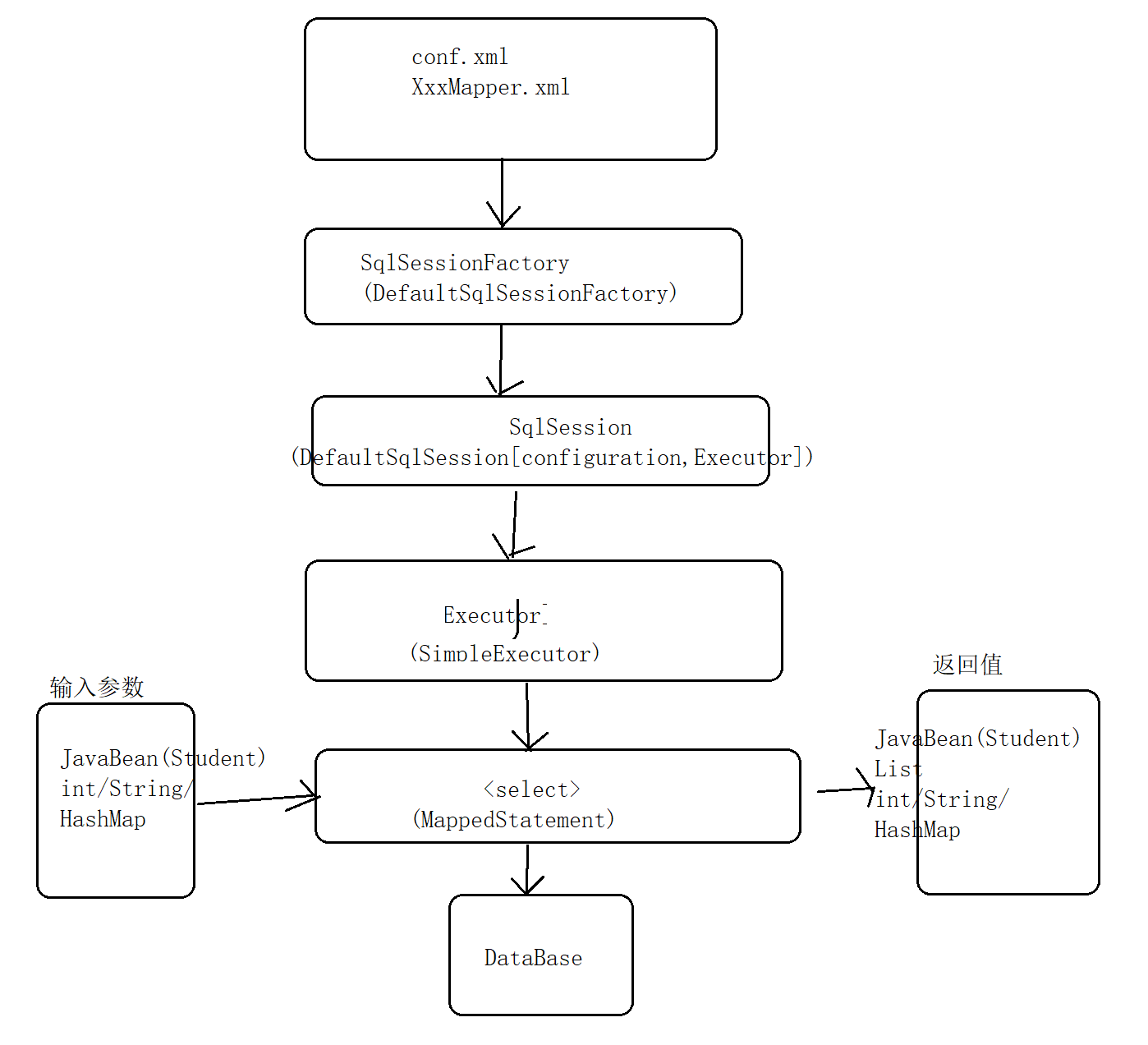
获取XxxMapper对象、执行
执行增删改查->MapperProxy/invoke()–>InvocationHandler :JDK动态代理接口
用到了 动态代理模式:增删改查 -> 代理对象 (MapperProxy对象) ->代理对象 帮我们“代理执行” 增删改查 ->
XxxMapper代理对象: MapperProxy对象
mapperMethod.execute(sqlSession,args) :实际调用增删改查的方法 ,依靠了sqlSession中的configuration和 executor..
处理增删改查方法的参数:method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);: 如果參數是0个,reutrun null ;如果参数是1,返回第一个 ; 如果有多个参数 放入map中
查询方法:selectOne() ->selectList() : configuration.getMappedStatement() 即获取到用于增删改查的对象
boundSql :将我们写的SQL 和 参数值进行了拼接后的对象,即最终能被真正执行的SQL
执行SQL 是通过Executor
如果缓存中没有要查询的内容,则进入数据库 真实查询:queryFromDatabase()
mybatis使用的jdbc对象是PreparedStatement
底层执行增删改查:PreparedStatement的execute()
MyBatis底层在执行CRUD时 可能会涉及到四个处理器:StatementHandler(处理对象PreparedStatement的控制器) 、 ParameterHandler(处理参数的控制器) 、 TypeHandler(类型转换的控制器) 、 ResultSetHandler(处理结果集的控制器)
XxxMapper包含:
SqlSession(configuration,executor,事务)、代理接口的对象(MapperInterface)、methodCache(存放查询缓存, 底层是CurrentHashMap)
自定义插件
四个处理:StatementHandler ParameterHandler ResultSetHandler TypeHandler
四大核心对象:StatementHandler ParameterHandler ResultSetHandler Executor
四大核心对象
- 都涉及到了 拦截器 用于增强
- 四大核心对象都包含了 该增强操作
自定义插件的编写逻辑: 根据MyBatis规则 编写一个 拦截器 ,在拦截器内部加入 自定义增强功能
步骤:
编写拦截器
public class MyInterceptor implements Interceptor {
//拦截
@Override
public Object intercept(Invocation invocation) throws Throwable {
System.out.println("拦截方法...intercept...");
Object proceed = invocation.proceed();//放行
return proceed;
}
@Override
public Object plugin(Object target) {//将拦截器中定义的 增强功能 和原来的核心对象 合并起来,称为最终的 核心对象
Object wrap = Plugin.wrap(target, this);
System.out.println("plugin...."+wrap);
return wrap;
}
@Override
public void setProperties(Properties properties) {
System.out.println("setProperties....");
}
}
编写签名注解
@Intercepts({
@Signature(type = StatementHandler.class , method ="query",args = {Statement.class, ResultHandler.class})
public class MyInterceptor implements Interceptor {
配置
<plugins>
<plugin interceptor="com.yanqun.my.interceptors.MyInterceptor">
<property name="name" value="zs"/>
<property name="age" value="23"/>
</plugin>
</plugins>
编写多个拦截器时,执行顺序 和 <plugins>配置顺序一致
插件
select * from student ->拦截器 增加where条件
编写拦截器
//query(Statement statement, ResultHandler resultHandler)
@Intercepts({
@Signature(type = StatementHandler.class , method ="parameterize",args = {Statement.class})
})
public class MyInterceptor implements Interceptor {
//拦截
@Override
public Object intercept(Invocation invocation) throws Throwable {
System.out.println("拦截方法...intercept...");
Object target = invocation.getTarget();//目标方法 : select * from student where stuNo = #{stuNo}
System.out.println("目标对象" +target);
MetaObject metaObject = SystemMetaObject.forObject(target);
// metaObject.getValue("参数..") ;
Object value = metaObject.getValue("parameterHandler.parameterObject");
System.out.println(value+"---------");
metaObject.setValue("parameterHandler.parameterObject",2);//11->1
Object value2 = metaObject.getValue("parameterHandler.parameterObject");
System.out.println(value2+"---------");
Object proceed = invocation.proceed();//放行
System.out.println(proceed);
return proceed;
}
@Override
public Object plugin(Object target) {//将拦截器中定义的 增强功能 和原来的核心对象 合并起来,称为最终的 核心对象
Object wrap = Plugin.wrap(target, this);
System.out.println("plugin...."+wrap);
return wrap;
}
@Override
public void setProperties(Properties properties) {
// System.out.println("setProperties....");
System.out.println("设置属性:"+properties); //设置属性...
}
}
目标对象target的包装后的产物 -> metaObject.getValue(“可以从target中获取”)
通过打印语句 可知,target就是 RoutingStatementHandler –> metaObject.getValue(“可以从RoutingStatementHandler中获取”)
->metaObject.getValue(“可以从RoutingStatementHandler中获取 :boundSql/parameterHandler”)
->->metaObject.getValue(“parameterHandler”)
metaObject.getValue("parameterHandler.parameterObject") //XxxMapper.xml中的sql语句中的参数值
metaObject.getValue("parameterHandler.boundSql") //XxxMapper.xml中的sql语句
–>只研究
metaObject.setValue("parameterHandler.parameterObject",2)//修改参数值
metaObject.setValue("parameterHandler.boundSql.sql","select * from book...") //修改sql语句
metaObject.setValue("parameterHandler.boundSql.parameterObject",2)
批量操作DML
sessionFactory.openSession(ExecutorType.BATCH ); --推荐的写法
<insert id="addStudent" parameterType="com.yanqun.entity.Student" databaseId="mysql">
insert into student(stuNo,stuName,stuAge,graName)
values(#{stuNo} , #{stuName},#{stuAge},#{graName})
</insert>
public abstract Integer addStudent(Student student);
SqlSession session = sessionFactory.openSession( );
StudentMapper studentMapper = session.getMapper(StudentMapper.class);//接口
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
for(int i=0;i<100000;i++) {
Student stu = new Student((int)(Math.random()*9000) +1000, "abc", 44, "xx");
studentMapper.addStudent(stu);
}
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println(end-start);
此时插入数据较慢
想变快则使用BATCH sessionFactory.openSession(ExecutorType.BATCH ); –推荐的写法
SqlSession session = sessionFactory.openSession( ExecutorType.BATCH);
StudentMapper studentMapper = session.getMapper(StudentMapper.class);//接口
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
for(int i=0;i<100000;i++) {
Student stu = new Student((int)(Math.random()*9000) +1000, "abc", 44, "xx");
studentMapper.addStudent(stu);
}
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println(end-start);
使用BATCH:
预编译SQL一次 ,其余DML 只需要设置参数值即可
insert into student(stuNo,stuName,stuAge,graName) values(#{stuNo} , #{stuName},#{stuAge},#{graName})
不使用BATCH:
预编译N次 ,每次DML都需要 执行完整的SQL
不推荐的方式: 拼接SQL
oracle:批量插入
a. create table 表 select ... from 旧表
b. insert into 表(...) select .. from 表 ;
c. begin ..(DML).. end ;
d. 数据泵、SQL Loader 、外部表
以 c. begin ..(DML).. end ;为例
begin
insert into student(stuno,stuname) values(1,"zs");
insert into student(stuno,stuname) values(1,"ls");
end ;
<insert id="addStudentOracle" databaseId="oracle">
<foreach collection="list" open="begin" close="end ;" item="student">
insert into student(stuno,stuname) values(#{student.stuNo},#{student.stuName}) ;
</foreach>
</insert>
void addStudentOracle (List<Student> students) ;
StudentMapper studentMapper = session.getMapper(StudentMapper.class);
List<Student> students = new ArrayList<>();
students.add( new Student(10,"zs") );
students.add( new Student(20,"ls") );
studentMapper.addStudentOracle(students);
–核心:将SQL拼接成oracle能够执行的SQL;
collection的参数必须是 collection或List
mysql:批量插入
insert into student(stuno,stuname) values(100,'zsx'),(200,'lsx'),(200,'lsx'),(200,'lsx')...... ;
<insert id="addStudentMySql" databaseId="mysql">
insert into student(stuno,stuname) values
<foreach collection="list" item="student" separator="," close=";" >
(#{student.stuNo},#{student.stuName})
</foreach>
</insert>
void addStudentMySql (List<Student> students) ;
StudentMapper studentMapper = session.getMapper(StudentMapper.class);
List<Student> students = new ArrayList<>();
students.add( new Student(510,"311zs") );
students.add( new Student(610,"311ls") );
studentMapper.addStudentMySql(students);
这种批量插入方式不推荐:
- 没有用到mybatis对批量插入的支持
- 不适合数据库迁移
- 如果大量数据,则会将 拼接的SQL语句拉的很长,而部分数据库 对SQL语句的长度有限制。
推荐:调存储过程、存储函数
mysql.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mydb?allowMultiQueries=true
myssql默认不支持接收多个分号(多条语句),这个可以修改默认设置
分页插件
PageHelper
- jar
- 配置conf.xml中
- PageHelper.startPage(2, 3);
配置conf.xml
<plugin interceptor="com.github.pagehelper.PageInterceptor">
<!-- 使用下面的方式配置参数,后面会有所有的参数介绍
<property name="reasonable" value="true"/>-->
</plugin>
<select id="queryStudents" resultType="com.yanqun.entity.Student" >
select * from student order by stuno
</select>
List<Student> queryStudents () ;
public static void queryStudents() throws IOException {
String resource = "conf.xml";
Reader reader = Resources.getResourceAsReader(resource);
SqlSessionFactory sessionFactory
= new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(reader);
SqlSession session = sessionFactory.openSession();
StudentMapper studentMapper = session.getMapper(StudentMapper.class);
/* 方式一 加入分页功能
Page<Object> page = PageHelper.startPage(2, 3);
*/
//pageInfo方式
PageHelper.startPage(2, 3);
/*
lambda形式
Page<Student> page = PageHelper.startPage(2, 3).doSelectPage(()-> studentMapper.queryStudents());
List<Student> list = page.getResult();
*/
// select * from student order by stuno ->拦截器
//select * from student order by stuno limit 6,3
List<Student> list = studentMapper.queryStudents() ;
for(Student student :list){
System.out.println(student);
}
//PageInfo方式
PageInfo<Student> pageInfo = new PageInfo<>(list);
System.out.println("当前页:"+pageInfo.getPageNum());
System.out.println("总数据量:"+pageInfo.getTotal());
System.out.println("总页码:" +pageInfo.getPages());
System.out.println("页面大小:" +pageInfo.getPageSize());
System.out.println("最开头那一页:"+ pageInfo.getNavigateFirstPage());
System.out.println("每一页的页号");
for( int pageNum : pageInfo.getNavigatepageNums()){
System.out.println(pageNum);
}
session.close();
}


